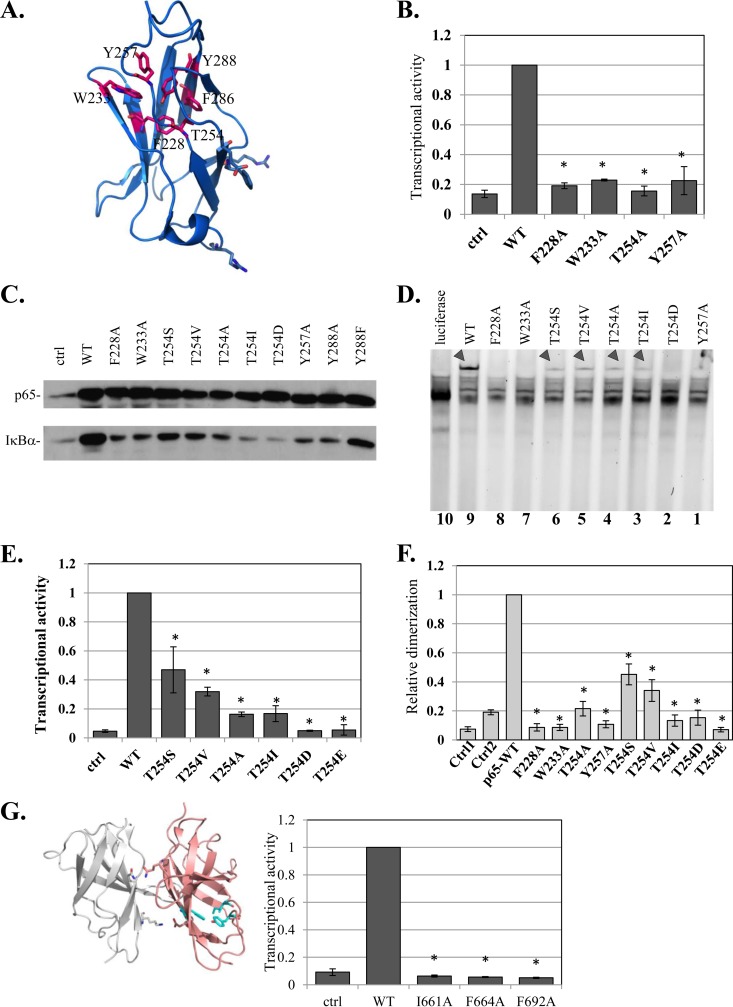
FIG 6.
Characterization of a highly conserved HCD as a dimerization scaffold in NF-κB and NFAT. (A) Structural illustration of a single central domain of p65 (aa 191 to 304) (PDB ID 1MY5) (14), with HCD residues marked. (B) Analysis of transcriptional activities of F228A, W233A, T254, Y257A, and Y288A HCD mutants as described for Fig. 1A. (C) Effects of HCD mutants on the expression of the IκBα gene, an endogenous target gene. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated HCD mutants and harvested 24 h posttransfection. The levels of endogenous IκBα in mock- and p65 variant-transfected cells were monitored by Western blotting. (D) The effects of HCD and T254 mutants on DNA binding were analyzed as described for Fig. 3D. The arrowheads point to the p65-DNA complexes. (E) The effects of T254 mutants on transcriptional activity were determined as described for Fig. 1A. The bars represent the means ± SE of the results of 4 independent experiments. (F) Analysis of dimerization activities of F228A, W233A, T254, Y257A, and Y288A HCD mutants using the split-RL assay as described for Fig. 1C. (G) (Left) Structural illustration of NFAT1 dimer (PDB ID 2O93) (34). Residues of the HCD that correspond to those mutated in NFAT2 are shown in cyan. (Right) WT NFAT2 and the HCD mutants were cotransfected into cells with a luciferase reporter gene driven by the IL-2 promoter and analyzed as described above. The results represent the means ± SE of the results of 4 independent experiments. The asterisks denote statistically significance differences (P < 0.05).