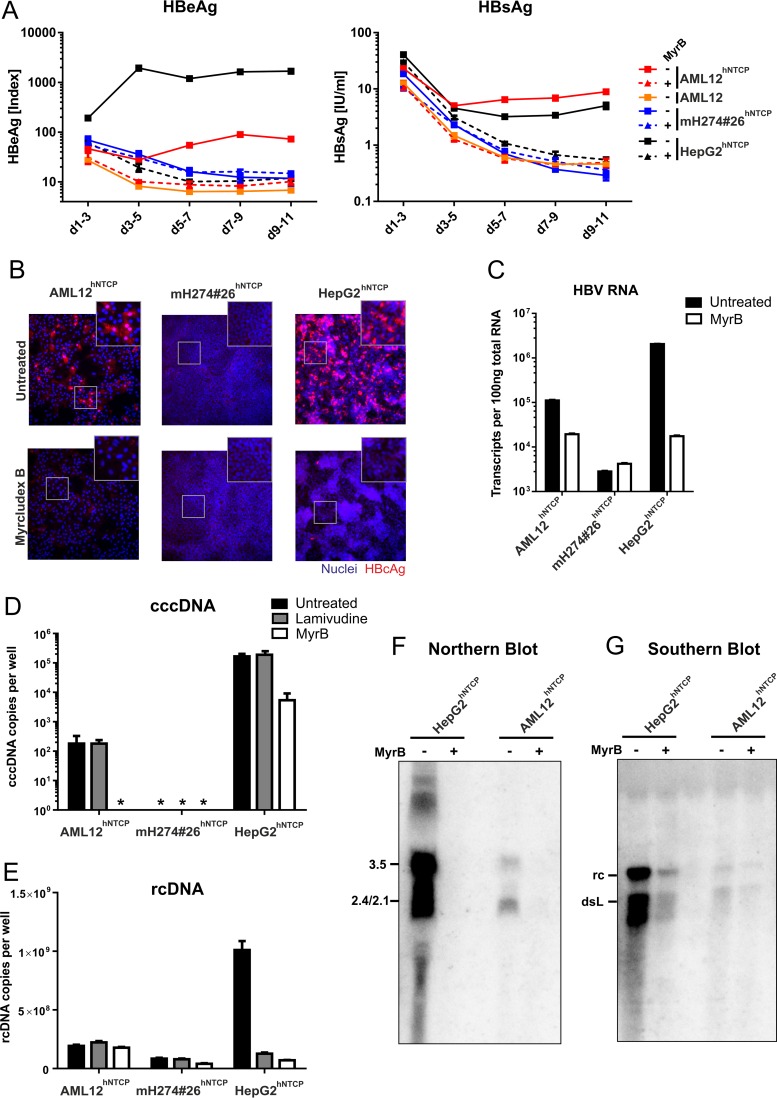
FIG 3.
HBV infection of stable hNTCP-expressing cell lines. AML12, AML12hNTCP, mH274#26hNTCP, and HepG2hNTCP cells were seeded in 24-well plates and infected 2 days later by inoculation with HBV at a multiplicity of genome equivalents (MGE) of 1,500 (genotype D, cell culture derived) in the presence of 4% PEG and 2% DMSO for 16 h as described previously (8). For entry inhibition, cells were treated with 500 nM Myrcludex B 30 min prior and during virus inoculation. (A) Supernatants of the cells were collected every second day, and secreted viral markers HBeAg (left) and HBsAg (right) were quantified by ELISA as previously described (8). Each data point represents the mean of the results of three biological replicates. d, day. (B) At day 11 postinfection, cells were fixed and immunostained with an antibody (Dako) recognizing viral HBcAg (red, ×200 magnification). (C) RNA from infected cells was extracted, reverse transcribed, and quantified using primers binding to the HBV core open reading frame (ORF), thereby detecting pregenomic, precore, and possibly spliced HBV RNA (4). (D and E) Total DNA was extracted from cells at day 10 postinfection. Lamivudine (10 μM) was added at day 3 postinfection. rcDNA was quantified with HBV-specific primers (E). Following digestion of rcDNA with T5 exonuclease (New England BioLabs), cccDNA (D) was specifically quantified using primers spanning the gap region (Bingqian Qu, unpublished data). Values below the limit of quantitation are marked by asterisks (*). (F and G) AML12hNTCP and HepG2hNTCP cells were seeded in 10 cm-diameter dishes and infected with HBV at an MGE of 1,500 in the presence or absence of 1 μM MyrB as described above. (F) Eight days after infection, total cellular RNA was extracted, separated on a 1.2% agarose gel, blotted on a nylon membrane, and analyzed with a 32P-labeled HBV-specific probe of genotype D (Northern blotting). (G) Ten days after infection, cytosolic DNA was extracted by treatment of the cells with NP-40 lysis buffer, centrifugation, proteinase K treatment of the supernatant, and subsequent phenol-chloroform DNA extraction. The DNA was separated on a 1.2% agarose gel and analyzed by Southern blotting as described above.