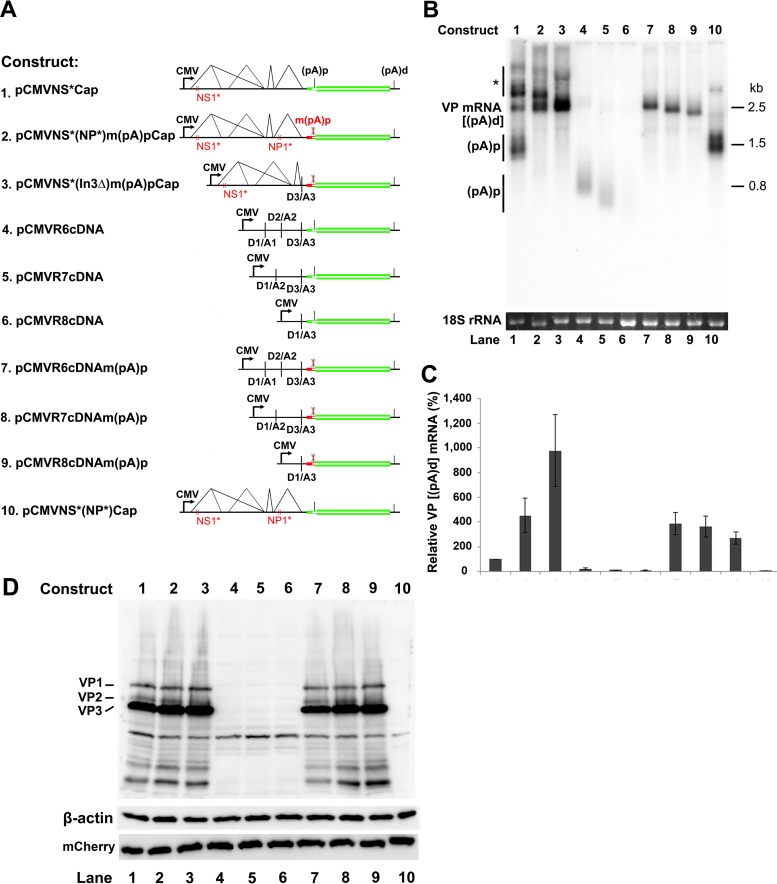
FIG 10.
Mutation of the (pA)p site enables VP mRNA production and capsid protein expression in the absence of NP1. (A) HBoV1 NSCap and cDNA constructs. HBoV1 NS and Cap genes and cDNA constructs are diagrammed, along with the pCMVNS*(NP*)Cap control. (B) Northern blot analysis of VP and (pA)p mRNAs. HEK 293 cells were transfected with constructs as indicated. The total-RNA samples were analyzed by Northern blotting using the NSCap probe. EB-stained 18S rRNA bands are shown. Detected bands of VP and (pA)p mRNAs are indicated on the left of the blot. The asterisk denotes various NS-encoding mRNAs. (C) Quantification of VP and (pA)p mRNAs on a Northern blot. The bands of VP and (pA)p mRNAs in each lane in panel B were quantified and normalized to 18S rRNA. The intensity of the VP mRNA band in lane 1 was arbitrarily set as 100%. Relative intensities were calculated for the bands of both VP and (pA)p mRNAs in the other lanes. Means and standard deviations were calculated from the results of three independent experiments. (D) Western blot analysis of capsid proteins. HEK 293 cells were transfected with plasmids as indicated. The cell lysates of each transfection were analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-VP antibody. The blot was reprobed with an anti-β-actin antibody. The lysates were also analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-HA antibody for mCherry expression.