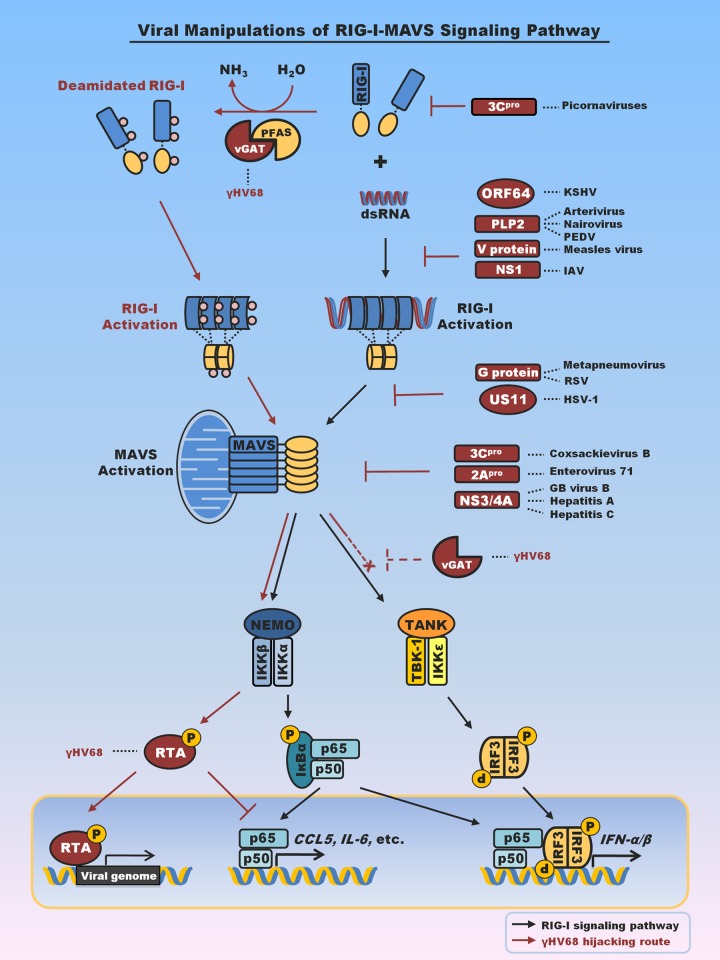
FIG 1.
Summary of viral factors that interfere with or hijack RIG-I-mediated innate immune signaling. Emphasis is placed on viral proteins that interfere with RIG-I or MAVS to evade antiviral cytokine production. Notably, viral proteins that target TBK-1 and IRF3 to block interferon production are not included here. vGAT proteins of KSHV and γHV68 recruit PFAS to deamidate and activate RIG-I. Activation of RIG-I and its downstream signaling events, specifically, those associated with IKKβ, result in p65 degradation and suppress inflammatory cytokine production (33–35). vGAT appears to blunt IRF activation by an unknown mechanism (indicated by dashed inhibition sign). PEDV, porcine epidemic diarrhea virus; IAV, influenza A virus; RSV, respiratory syncytial virus; HSV-1, herpes simplex virus 1; Hepatitis A, hepatitis A virus; Hepatitis C, hepatitis C virus; GB virus, hepatitis G virus; pro, protease; NEMO, NF-κB essential modulator; TANK, TRAF family member-associated NF-κB activator. RTA, replication and transcription activator.