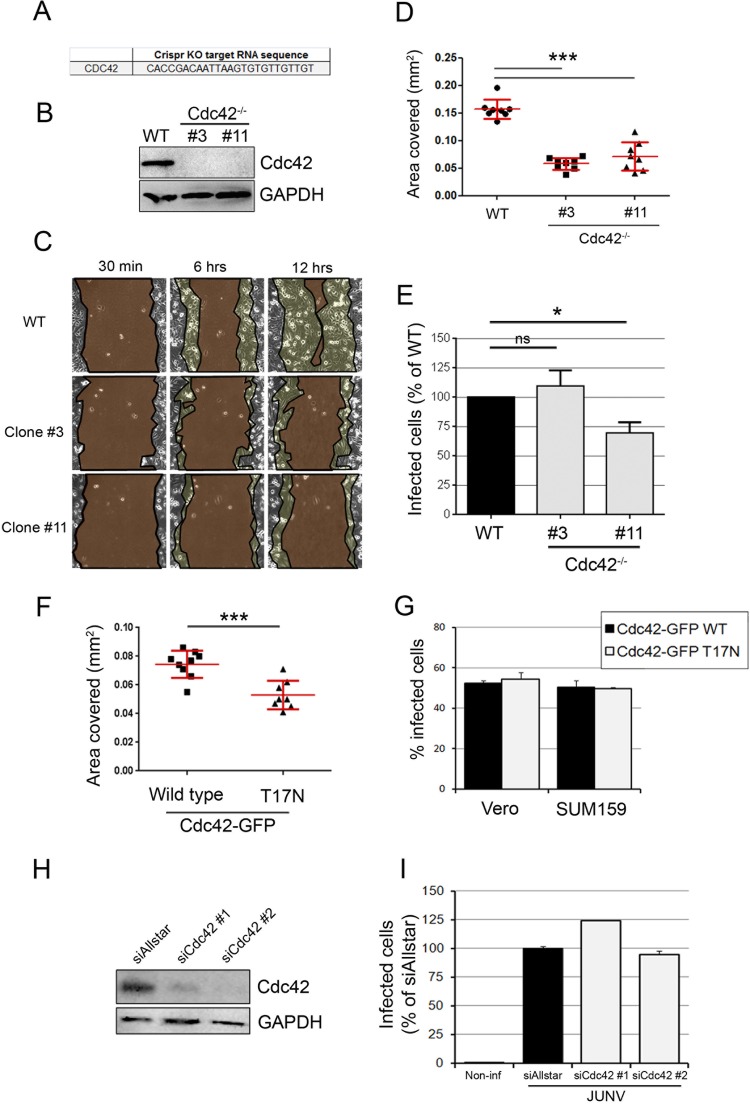
FIG 4.
JUNV enters cells in a Cdc42-independent manner. (A) Sequence of the gRNA targeting Cdc42 inserted into the LentiCRISPR vector. KO, knockout. (B) SUM159 cells subjected to Cdc42 knockout by transduction of a lentiviral vector were selected for 15 days postransduction, and monoclonal populations were isolated. The Cdc42 protein expression level from the wild type (WT), clone 3, and clone 11 was measured by Western blotting using an anti-Cdc42 antibody and revealed by use of a secondary antibody coupled to horseradish peroxidase. An anti-GAPDH antibody was used as a loading control. Even with a long exposure time, no Cdc42 protein could be detected in clones 3 and 11. (C) Wound healing assay of wild-type, Cdc42−/− clone 3, or Cdc42−/− clone 11 SUM159 cells that had been plated to confluence on the day before the scratch. Cells migrating to close the wound were imaged over a 12-h period. Micrographs show the same field of view at different time points after wounding for each cell type. The regions highlighted in dark brown indicate the surface area of the wound, which became smaller with time. The light brown regions delineate the cells that migrated, closing the wound, and correspond to the area covered (in millimeters squared). (D) The plot represents the area covered by the cells at 6 h after wounding compared to that covered at 30 min after wounding. Each dot represents a single movie, and eight movies were acquired per condition. Red lines, means ± SDs. Statistical analyses for significance were performed using the two-tailed Student t test to compare the results for the wild type and either clone 3 or clone 11. ***, P < 0.0001. (E) Wild-type or Cdc42−/− SUM159 cells (clones 3 and 11) were infected with JUNV for 16 h, and the percentage of infected cells was measured by flow cytometry. The data are normalized to the percentage of infected wild-type cells. Error bars are the means ± SDs from eight independent experiments, in which the results for at least 5,000 cells per condition were acquired in duplicate. Statistical analyses were performed using the two-tailed Student t test and showed no significant differences (ns) between the wild type and clone 3 (P = 0.49) and significance differences between the wild type and clone 11 (*, P = 0.013). (F) Wound healing assay, as exemplified in panel C, of SUM159 cells transfected with wild-type Cdc42-EGFP or a dominant negative mutant counterpart, Cdc42-EGFP T17N. Statistical analysis was performed using the two-tailed Student t test and showed a significant difference. ***, P < 0.0001. (G) Vero or SUM159 cells transfected to overexpress the Cdc42-EGFP wild type (black bars) or the T17N mutant (gray bars) were infected with JUNV for 16 h, and the percentage of infected cells in the EGFP-positive cell population was measured by flow cytometry. Error bars are the means ± SDs from duplicate experiments with at least 10,000 cells per condition. (H, I) Cdc42 protein expression was knocked down in Vero cells by transfecting two individual siRNAs targeting Cdc42 mRNA. (H) At 2 days posttransfection, the silencing efficiency was estimated by Western blotting to be 82% (siCdc42#1) and 92% (siCdc42#2). (I) In parallel, a subset of these cells was infected with JUNV for 16 h, and the percentage of infected cells was assessed by flow cytometry. Error bars are the means ± SDs from duplicate experiments with at least 10,000 cells per condition.