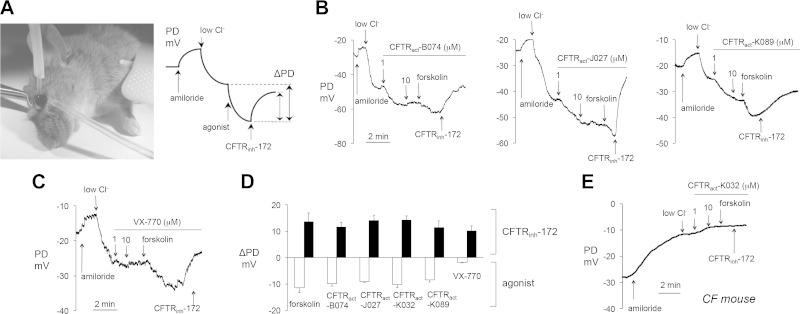
Figure 3.
PD measurements of CFTR activators at the ocular surface in live mice. A) Left: photograph of an anesthetized mouse demonstrating ocular surface perfusion for PD measurement. The perfusion catheter, attached to the measuring electrode, is oriented perpendicular to the ocular surface. Cross-clamping forceps retract the upper eyelid to expose cornea and bulbar/palpebral conjunctiva for perfusion. The reference electrode is grounded via subcutaneous butterfly needle. Right: Idealized PD tracing for a typical experiment testing CFTR activity. B) Representative ocular surface PD measurements in WT mice. (Solution compositions are detailed in ref. 11). Concentrations: amiloride, 100 μM; FSK and CFTRinh-172, 10 μM; test compounds, 1–10 μM, as indicated. C) Study as in B, but with VX-770, 1–10 μM, as indicated. D) Summary of ΔPD in WT mice produced by FSK (20 μM), or test compounds or VX-770 (each 1 μM). PDs were recorded in the presence of 100 μM amiloride and an outward apical Cl− gradient. Means ± sem (n = 8–20 eyes per agonist tested). E) Representative ocular surface PD measurements in CF mouse. Study as in (B, C) CFTRact-K032 (1–10 μM, as indicated).