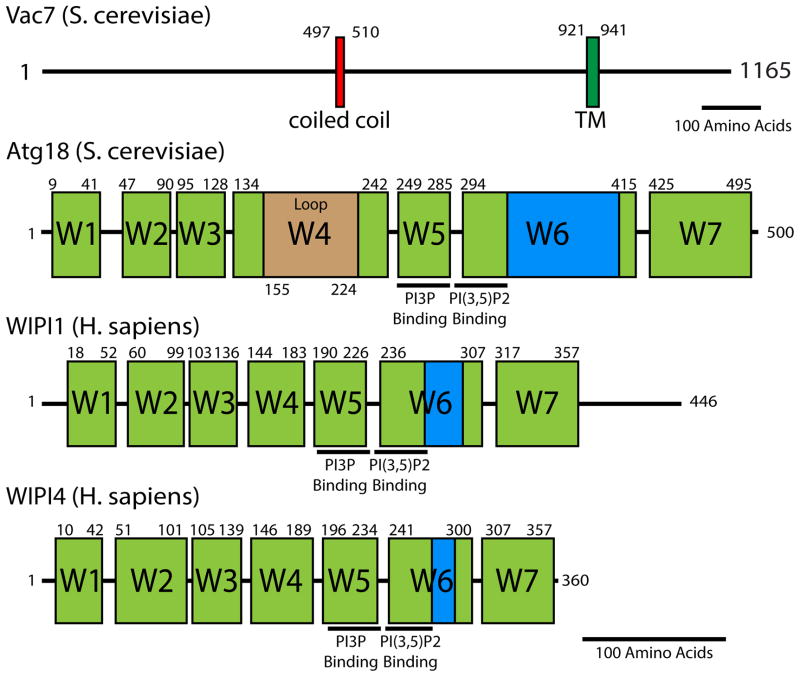
Figure 3. Domain architecture of Vac7 and Atg18.
Vac7 is found only in some fungi. Atg18 is similar to mammalian WIPI1 and WIPI2; however, it is not known if these WIPI proteins regulate PIKfyve. For Vac7, boundaries of each domain were determined using a combination of Jpred4 secondary structure prediction and ClustalW multiple sequence alignment. Vac7 contains a coiled-coil domain (80% certainty using COILS) and a transmembrane domain. Atg18, WIPI1, and WIPI4 domain boundaries were determined from ClustalW multiple sequence alignment with Hsv2—a related protein where high-resolution structures are available [31, 75, 76]. Seven WD40 blades are depicted in green. A hydrophobic lipid-associated region is highlighted in blue. Beige Atg18 Loop is a predicted unstructured region between beta sheet 2 and 3 of blade 4. WIPI2 (not depicted) is structurally similar to WIPI1 and both contain an unstructured C-terminal tail with 31% similarity to each other. WIPI3 (not depicted) is structurally similar to WIPI4. Residue pockets predicted to bind PI(3)P and PI(3,5)P2 are highlighted for ATG18, WIPI1, and WIPI4. That these regions are conserved indicates that Atg18, WIPI1, WIPI4 as well as their paralogs likely interact with phospholipids in a similar manner. Black lines represent 100 amino acids.