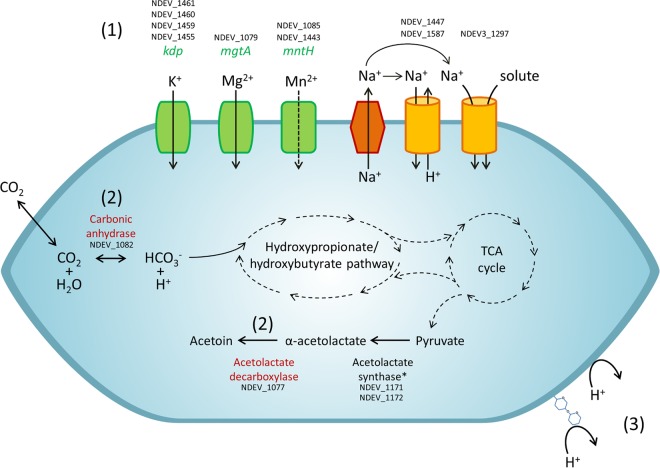
FIG 1.
Predicted mechanisms of cytoplasmic pH regulation in “Ca. Nitrosotalea devanaterra” based on the presence of putative functional genes in the genome. (1) Cation influx and proton efflux. kdp, potassium transporting P-type ATPase gene; mgtA, putative magnesium-transporting P-type ATPase gene; mntA, NRAMP-type divalent cation transporter (two copies) gene, Na+/solute transporter, Na+/hydrogen exchanger (two copies). (2) Proton consumption by metabolism: acetolactate decarboxylase, carbonic anhydrase. (3) Reduced permeability of the cell wall/cell membrane: cell surface glycosylation, GDGT-4-dominated membrane.