FIG 1.
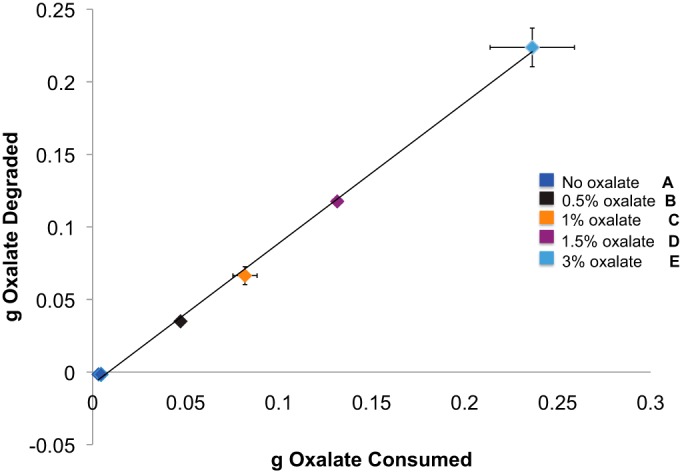
The amount of oxalate consumed is correlated with the amount of oxalate degraded (estimated from the differential between oxalate consumed and the total oxalate excreted in the urine and feces). The data were analyzed with a repeated-measures Pearson correlation (r = 0.99845, P < 0.001). The oxalate consumed also increased significantly with increasing oxalate consumption as determined by a repeated-measures ANOVA with a post hoc Holm-corrected Tukey analysis (the statistical groups are shown by bold letters).
