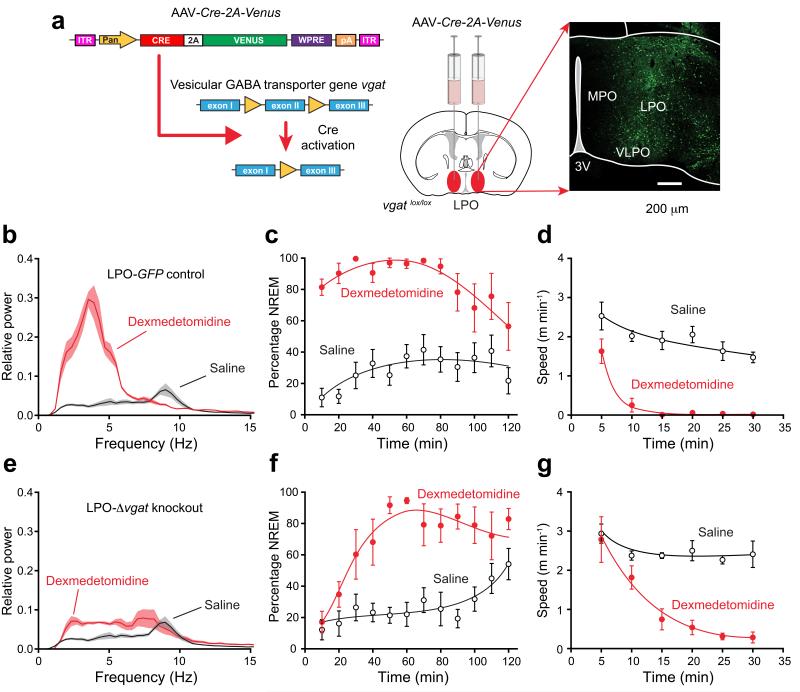
Figure 7.
Selective knockout of the GABA vesicular transporter gene (vgat) in the PO hypothalamic area (LPO-Δvgat mice) slows the transition to dexmedetomidine-induced sleep. (a) Cre recombinase, produced from an AAV transgene, deletes exon 2 of the vgat gene33 following AAV-Cre-2A-Venus bilateral injection into the LPO area of vgatlox/lox mice. The image on the right shows the extent of AAV expression, as detected by staining with EGFP antisera. (b) EEG power spectra ten minutes after dexmedetomidine (100 μg kg−1 – red line) or saline (black) injection in control mice (n=8) expressing AAV-GFP in the LPO (LPO-GFP mice; n=6). Lighter shaded envelopes indicate the s.e.m. (c) Percentage of time scored as NREM sleep after dexmedetomidine (100 μg/kg; filled circles, n=6) was significantly greater (two-way ANOVA, P<0.0001) than in saline (open circles, n=8) in LPO-GFP control mice. (d) Speed in open field 30 min after dexmedetomidine (100 μg kg−1; filled circles, n=7) was significantly less (two-way ANOVA, P<0.0001) than in saline (open circles, n=6) in LPO-GFP control mice. (e) EEG power spectra ten minutes after dexmedetomidine (100 μg/kg – red line; n=6) or saline (black) injection in mice (n=8) expressing AAV-Cre-2A-Venus in the LPO (LPO-Δvgat mice). (f) Percentage of time scored as NREM sleep after dexmedetomidine (100 μg kg−1; filled circles, n=6) was significantly greater (two-way ANOVA, P<0.0001) than in saline (n=8) in AAV-Cre-2A-Venus mice. (g) Speed in open field 30 min after dexmedetomidine (100 μg kg−1; filled circles, n=6) was significantly less (two-way ANOVA, P<0.0001) than in saline (open circles, n=8) in LPO-Δvgat mice. For all panels the error bars represent s.e.m.