FIGURE 1.
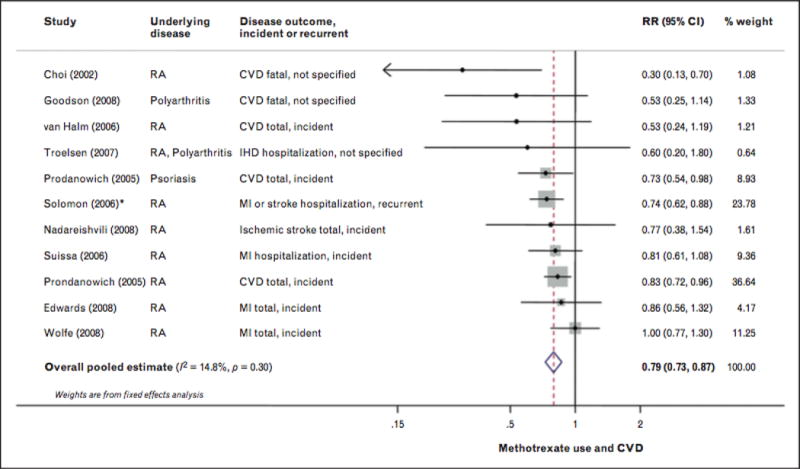
Risk for cardiovascular disease associated with methotrexate use, including eight prospective and two retrospective cohort studies, 66334 participants and 6235 events. Random-effects meta-analysis was used to calculate the overall pooled RR, in the presence of statistical between-study heterogeneity (P>0.10]. Solid diamonds and lines are study-specific RRs ond 95% Cls, respectively; the size of each box is weighted by the inverse variance of each study. Dashed line and open diamond are pooled RR and 95% CI, respectively, combining each study-specific RR. *Assessed other RA medication compared with methotrexate as the reference group. The RR of methotrexate versus other RA medications wos calculated by pooling the inverse RRs of all other RA medications, using fixed-effects meta-analysis. CI, confidence interval; IHD, ischaemic heart disease; RA, rheumatoid arthritis. Adapted from [85■■].
