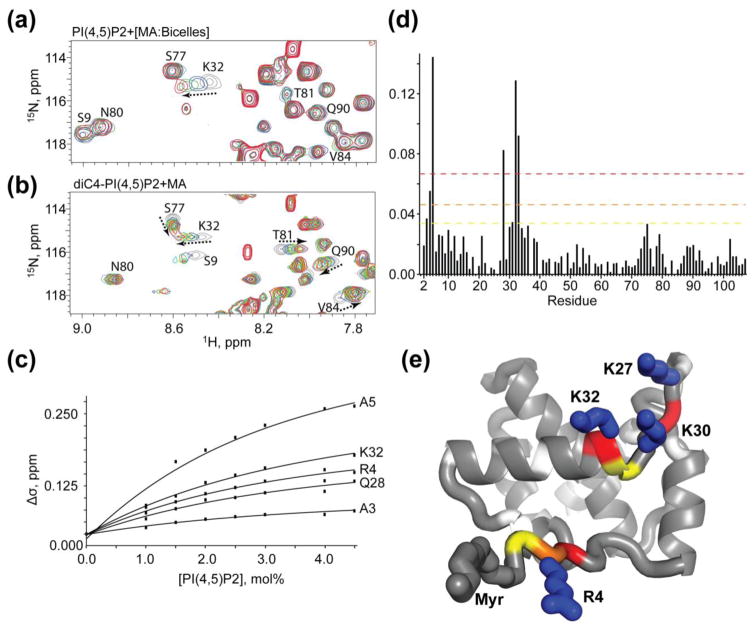
Figure 8.
Titration of PI(4,5)P2 into MA:bicelles does not support an extended lipid model. Overlay of 2D 1H-15N HSQC spectra of MA upon titration with (a) bicelle-associated native PI(4,5)P2 and (b) soluble tr-PI(4,5)P2 molecules. Colors correspond to tr-PI(4,5)P2:MA 0:1, grey; 2:1, blue; 4:1, green; 8:1, yellow; 16:1, red; native PI(4,5)P2 0 mol%, grey; 1 mol%, blue; 2 mol%, green; 3 mol%, red. (c) 15N NMR chemical-shift titration data, which fit to 1:1 binding isotherms (Kdapparent = 2.6 ± 0.4 mol%). (d) Histogram displaying the chemical shift perturbation of amide signals caused by addition of 3 mol% PI(4,5)P2 in bicelles to 15N labeled MA. Colors correspond to 1 (yellow), 2 (orange), and 3 (red) standard deviations from the mean noise (below 0.038 ppm). (e) Ribbon representation of MA highlighting the residues corresponding to panel d thresholds that experience to largest perturbation upon titration of PI(4,5)P2 in bicelles (R4, A5, Q28 (adjacent to K27), K30, and K32). Side chains of basic residues that contribute to electrostatic interactions with the acidic phosphates on the inositol head group are labeled.