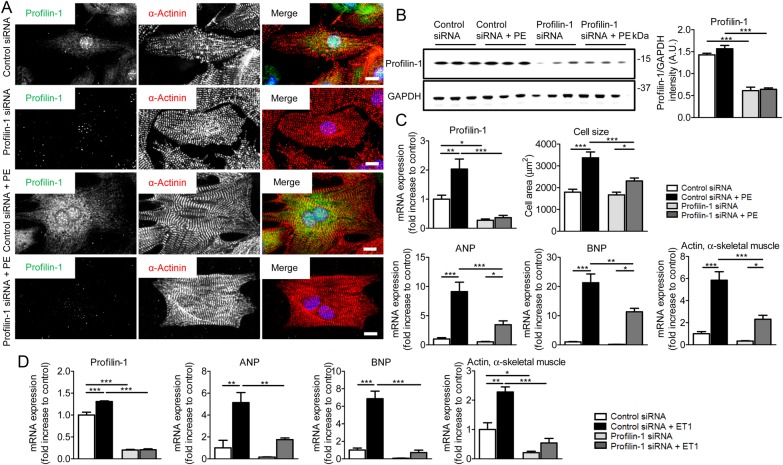
Figure 6.
Silencing of Pfn1 attenuates hypertrophic signalling in NRVMs. (A) Representative confocal images of control and PE-stimulated NRVMs. NRVMs were treated with control siRNA or Pfn1 siRNA. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Profilin-1 was dramatically reduced in response to Pfn1 siRNA. Scale bar, 10 μm. (B) Western blot analysis showed significantly decreased profilin-1 levels after the treatment of NRVMs with Pfn1 siRNA (n = 3, ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test). (C) Transcript levels of Pfn1 in PE-stimulated NRVMs were increased compared with control, and treatment with Pfn1 siRNA significantly reduced mRNA levels (n = 4, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test). Cell surface area increased significantly upon treatment with PE and was diminished upon profilin-1 silencing (n = 20–29, *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test). Transcription of the hypertrophic markers ANP, BNP, and skeletal muscle actin was significantly reduced after Pfn1 silencing in PE treated cells (n = 4, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test). (D) NRVMs that were treated with Pfn1 siRNA and stimulated with ET1 exhibited significantly reduced ANP, BNP, and skeletal α-actin mRNA levels compared with control siRNA-treated cells (n = 3, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni post hoc test).