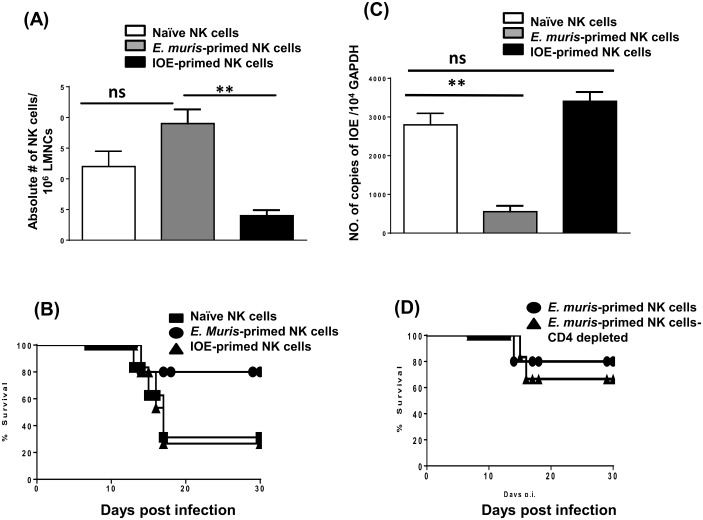
Fig 14. NK cells in E. muris-primed mice acquire adaptive features and a memory phenotype.
CD45+NK1.1+CD3- NK cells were purified from the spleen and liver collected on day 21 from E. muris-primed mice, and ~5–8 x 105 splenic and hepatic NK cells (1:1 ratio) were transferred into naïve Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice. Control mice were naïve Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− hosts receiving naïve NK cells. The numbers of memory-like NK cells, as measured by flow cytometry, in recipient Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice that received naïve, E. muris-primed or IOE-primed NK cells (A). Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− hosts receiving E. muris- primed NK cells survived longer than mice receiving naïve or IOE-primed NK cells following E. muris infection (B). Bacterial burden in the livers of recipient Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice at day 7 following E. muris infection (C). Depletion of contaminating donor CD4+T cells in recipient Rag2−/−Il2rg−/− mice did not influence mice survival following E. muris infection (D). ** indicate P < 0.01. Data are presented as the means ± SD of 3 mice/ group and are representative of two independent experiments. Data are presented as means ± SD from three mice per group. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments.