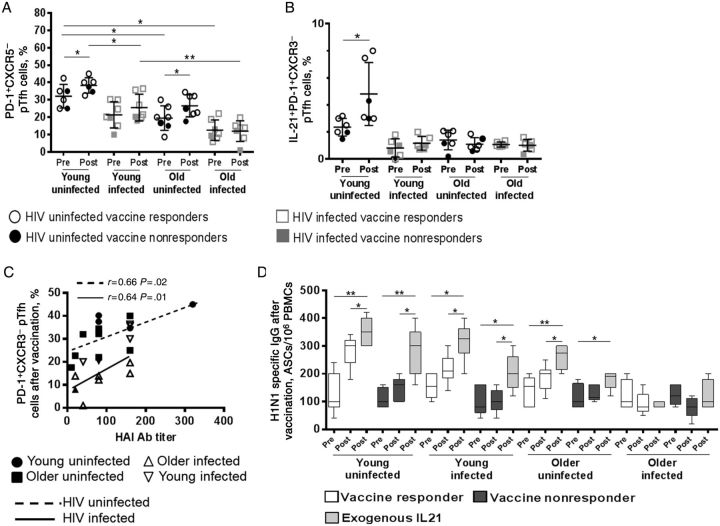
Figure 4.
Association between CXCR3− peripheral T-follicular helper (pTfh) cells with antibody (Ab) responses to influenza vaccination in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected and HIV-uninfected participants. Cryopreserved peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from HIV-uninfected participants (7 young participants and 7 older participants) and HIV-infected participants (7 young participants and 7 older participants) before and after vaccination were stained with monoclonal Ab to determine frequencies of the programmed cell death 1–expressing (PD-1+) CXCR3− pTfh-cell subset (gated from CD4+CD45RO+CXCR5+ cells) by flow cytometry (A). B, Frequencies of interleukin 21–expressing (IL-21+) PD-1+CXCR3− pTfh cells at baseline and after vaccination in all groups following H1N1 antigen (5 µg/mL) stimulation. C, Association between frequencies of PD-1+CXCR3− pTfh-cell subset and hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) titers after vaccination. D, PBMCs obtained from participants before and after vaccination were cultured for 5 days with H1N1 antigen with or without recombinant IL-21 (50 ng/mL). After 5 days, cells were analyzed by a B-cell enzyme-linked immunosorbent spot assay. Abbreviation: IgG, immunoglobulin G.