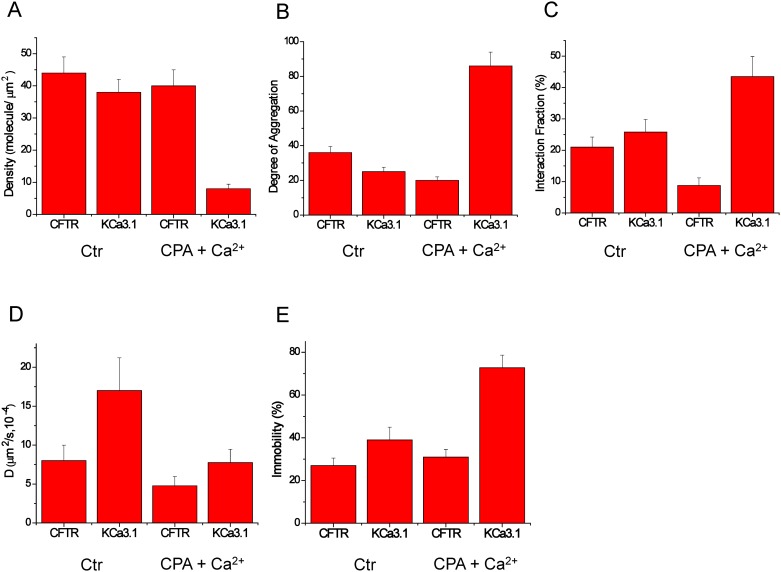
Fig 4. CFTR/KCa3.1 interactions modulated by internal Ca2+.
A: CFTR and KCa3.1 number densities (molecule/μm2) under control and Ca2+ influx conditions. KCa3.1 number density dramatically decreases (4-fold) during Ca2+ influx induced by pretreatment with CPA (cyclopiazonic acid) followed by exposure to extracellular Ca2+, consistent with either internalization of this channel or its clustering. B: CFTR and KCa3.1 degree of aggregation (DA) under control and Ca2+ influx conditions. KCa3.1 degree of aggregation increases significantly (4-fold) during Ca2+ influx. The 4-fold decrease in number density is accounted for by the 4-fold increase in KCa3.1 cluster size (DA). C: Significant increase in the fraction of KCa3.1 interacting with CFTR in response to a rise in intracellular Ca2+ concentration. Protein/protein interactions occurred on a slow time scale (D) and most interactions involved molecules that were immobilized on the plasma membrane (E). Statistical analysis based on n = 62 cells for control experiments and n = 21 cells for measurements in CPA+ Ca2+ conditions.