Figure 2.
A Subset of CD81 Interaction Partners Is Required for HCV Infection
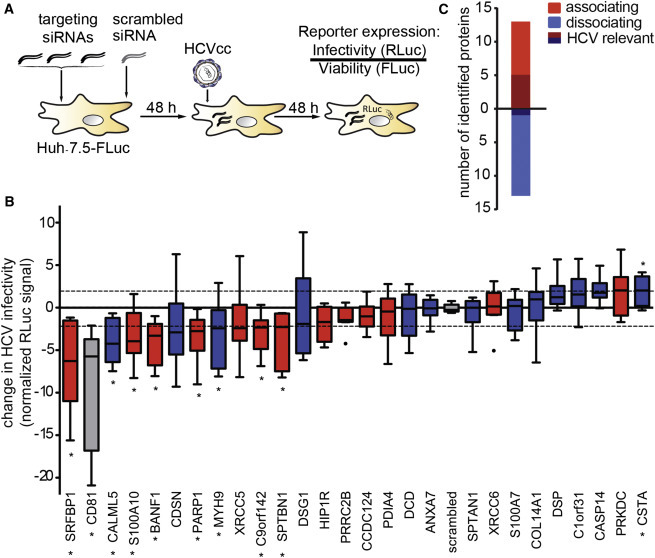
(A) Outline of the RNAi screen on transient CD81 interaction partners relevant for HCV infection.
(B) Functional RNAi follow-up screen on 26 selected transient CD81 interaction partners identifies nine putative host factors. We silenced the indicated transcript with a pool of three siRNAs in Huh-7.5 FLuc cells, infected 48 hr later with Renilla luciferase reporter HCV (JcR2A), and determined cell viability and HCV infectivity 48 hpi. Shown is the RLuc signal after normalization for cell viability and plate effects. Eight siRNA pools significantly decreased and one increased HCV infectivity (p ≤ 0.05; abs [z score] ≥ 2; ∗). Associating factors (red), dissociating factors (blue), CD81 and scrambled controls (gray) are shown. Box and whisker plot of nine biological replicates is shown.
(C) The combined SILAC co-IP RNAi strategy reveals a bias for CD81-associating factors to act as HCV host factors. Out of 26 HCV-dependent CD81-binding partners, six decreased HCV infectivity upon RNAi with a minimum transcript reduction of 75% (shaded color). See also Figure S2 and Tables S5 and S6.
