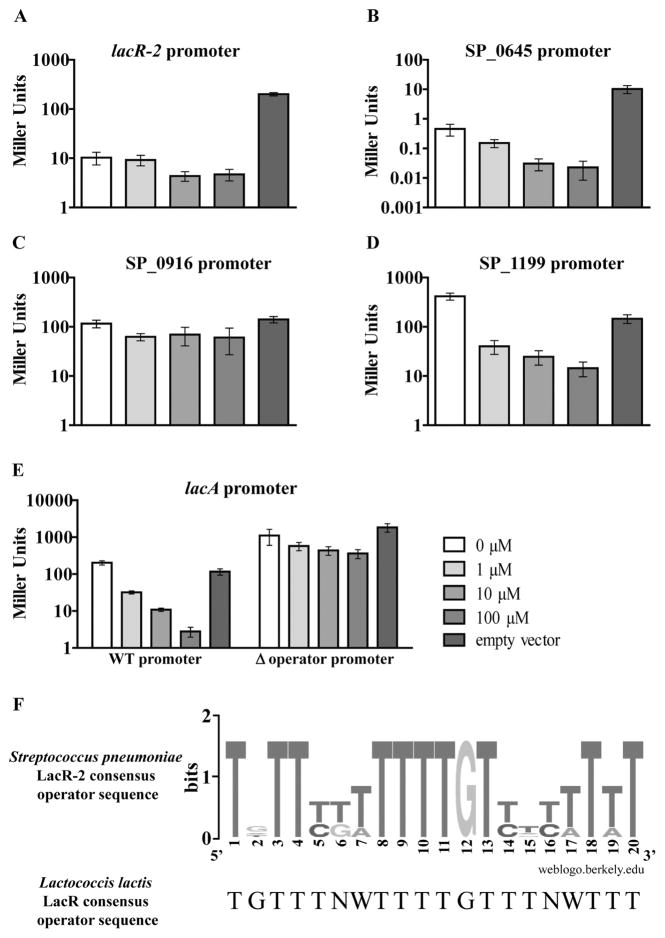
Fig. 6. Validation of predicted LacR-2 operator sequences in Escherichia coli MG1655.
A–E. A LacZ-based reporter system in the heterologous host E. coli was used to validate the predicted LacR-2 operator sequences listed in Table 2. This system consisted of two parts: cloning LacR-2 regulated promoter regions in place of lacZ’s endogenous transcriptional regulation elements in E. coli MG1655 and IPTG-inducible expression of lacR-2 from a plasmid in these strains. The Miller assay was used to measure LacZ activity of the resulting strains under increasing concentrations of IPTG (shown by increasing intensity of gray). To determine auto-regulation, the lacR-2 promoter with both predicted operator sequences was tested in A. To determine direct regulation of SP_0645, SP_0916 and SP_1199, their respective promoter fusion strains were tested in part B, C and D respectively. To test for direct regulation of the lacA operon, its promoter fusion strain and the isogenic operator deletion version were tested in E. For each section, bars represent the average of six biological replicates with error bars representing the standard error of the mean. F. These confirmed operator sequences were used to generate a consensus sequence logo. Searching the TIGR4 genome for this revised sequence predicted no additional sites beyond the sites that had already been validated by this assay.