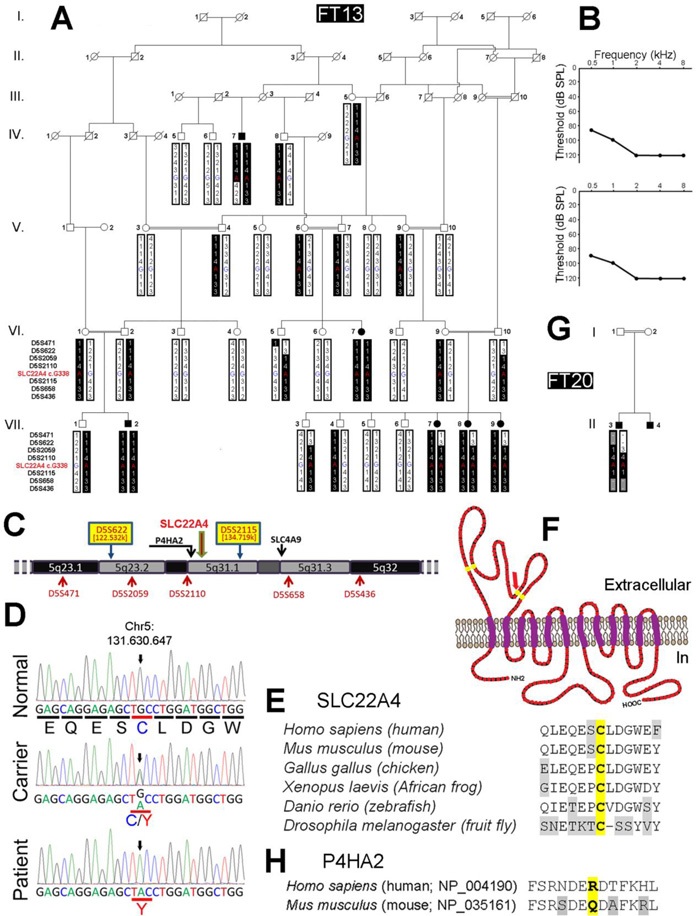
Figure 1.
Molecular genetic and structural analysis of SLC22A4 mutation. (A) Homozygosity mapping of recessive isolated HL-causing gene in consanguineous family FT13. Family FT13 pedigree showing the co-segregation of HL with a haplotype reconstructed between microsatellite markers D5S471 and D5S436, including the genotype of SLC22A4 c.G338 position within chromosomal region 5q23.1–q32. Key recombination events leading to heterozygosity in deaf individual IV:7 telomeric to marker D5S2115, and in deaf individuals VII:7, VII:8 and VII:9 centromeric to marker D5S622 allowed us to map the causative gene between these two markers within a 12.2 cM region. (B) Audiograms of deaf individuals VII:7 (upper panel) and IV:7 (lower panel). Audiograms of other deaf individuals in the family were not significantly different. Hearing loss is bilateral and profound, with a very similar pattern for both ears. (C) Physical map of chromosomal region 5q23.1–q32 showing the location of candidate genes SLC22A4, P4HA2 and SLC4A9 where homozygous aminoacid variations were found by whole exome sequencing on patient VII:7. (D) Electrofluorograms of hearing wild type individual (VII:6), hearing carrier individual (VI:9) and deaf individual (VII:7) showing the identification of c.338G>A nucleic substitution (ch5:131,630,647) causing SLC22A4 p.Cys113Tyr amino acid substitution in FT13 family. Sanger sequencing on genomic DNA samples from all available FT13 family deaf and hearing members confirmed the segregation of c.338G>A with HL. (E) Interspecies alignment of amino acid sequences around residue p.Cys113 of SLC22A4 showing its high conservation. (F) Predicted dodeca-transmembrane protein SLC22A4 secondary structure. Yellow residues are highly conserved Cysteine residues predicted to be essential for the formation of the large extracellular loop located between TM1 and TM2; red arrow pinpoint to residue p.Cys113. (G) Pedigree of consanguineous family FT20 showing the haplotype and the homozygous OCTN1 homozygous c.338G>A mutation in the deaf child. (H) Alignment of amino acid sequences of human P4HA2 and mouse P4ha2 around residue p.Arg439 of P4HA2 (NP_004190) showing no conservation in mouse orthologous sequence (NP_035161) corresponding to residue p.Gln441 that is identical to substitution pArg439Gln found in FT13, therefore concluded as a non-pathogenic polymorphism.