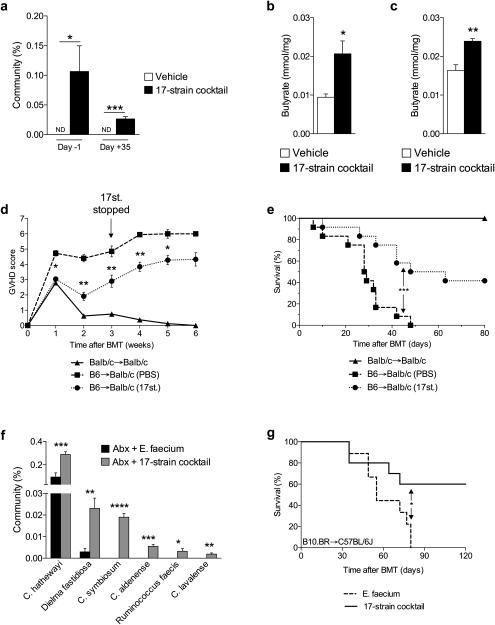
Figure 6. Rationally altering the commensal microbiota reduces GVHD.
(a) 16S rRNA-encoding gene sequencing of stool for percent of 17 Clostridal strains in total GI community on day −1 and day +35, relative to allogeneic (C57BL/6J → BALB/c) BMT on day 0. Vehicle or 17-strain cocktail were administered to recipients every other day via intragastric gavage beginning day −14 and continued through day +21, relative to BMT. ND = not detected. (b)-(c) Recipients of allogeneic BMT gavaged with vehicle or colonized with 17-strain cocktail were sacrificed 21 days following BMT. (b) Intestinal luminal contents (stool) and (c) intestinal tissue were harvested and analyzed via GC/MS. (d) GVHD clinical score and (e) survival following syngeneic (BALB/c → BALB/c) and allogeneic (C57BL/6J → BALB/c) BMT with 17-strain administration, compared to vehicle control; syngeneic n=6, n=12 mice per allogeneic group. (f)-(g) Obligate anaerobes of C57BL/6J (H-2b) mice were targeted with antibiotic mixture (ampicillin 5 mg, metronidazole 4 mg, clindamycin 5 mg, and vancomycin 5 mg) by intragastric gavage for 6 days followed by colonization with cocktails of E. faecium or 17-strains, 4 and 6 days later and subsequently used as recipients of allogeneic BMT (B10.BR → C57BL/6J). 17-strain Clostridial cocktail used at the University of Michigan and Memorial Sloan Kettering was identical. (f) 16S gene sequencing was performed on stool collected from recipients of allogeneic BMT on day −1, relative to BMT. (g) Survival of allo-BMT recipients of intragastric gavage of 17 Clostridial strains cocktail; Recipients of E. faecium n=9 , 17-strain n=10 mice. *P < .05; **P < .01; ***P < .0001 of students t-test a – c, f; Mantel-Cox log-rank test d, e, g. Bars and error bars represent the means and standard errors of the mean, respectively.