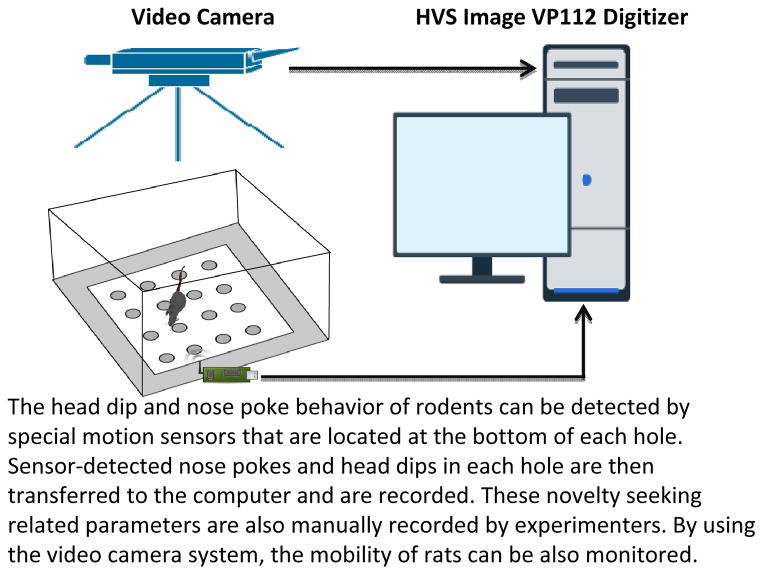
Figure 2.
Illustration of hole-board test, a free-choice novelty-seeking behavioral task test for rodents. The apparatus is an enclosed box with equally spaced holes; the following behavioral parameters are measured during the test session: head dipping, nose poking, rearing, and grooming. Head dipping and nose poking represent exploratory behaviors that are independent of locomotor activity. Compared with the open field arena test (see Figure 1), the hole-board test more directly measures novelty-seeking behavior, because it has not been shown to elevate the corticosterone concentration. The hole-board test is advantageous to researchers studying novelty-seeking behavior in naïve rodents.