FIGURE 8.
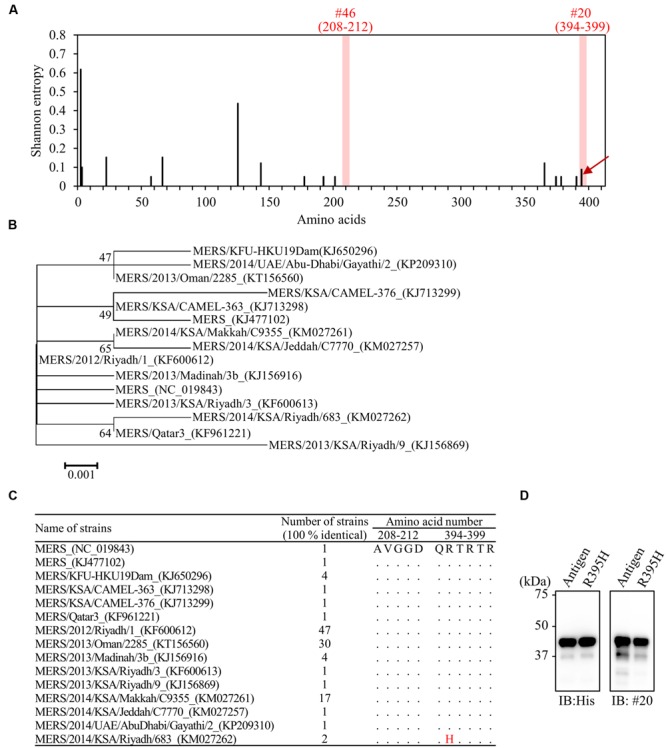
Comprehensive detection of MERS-CoV isolates by the generated mAbs. (A) Distribution of amino-acid variation of NP in 113 MERS-CoV strains. Shannon entropy, as a quantitative measure of variation, was calculated for each amino-acid residue of MERS-NP. Arrow indicates amino-acid mutation in the epitope of mAb (#20) from two MERS-CoV strains. (B) Phylogenetic analysis of MERS-CoV based on multiple sequence alignment of NP. The unrooted phylogeny is generated from amino-acid sequence alignments of nucleocapsid proteins based on the maximum-likelihood method. Sequences with identity of 100% are removed from the dataset. Bootstrap values (1,000 replicates) are indicated around the branches. The scale bar represents amino-acid substitutions per site. (C) Identification of amino-acid substitution in the antigenic epitope in 15 identical strains. Dots indicate sequence identity relative to the prototype strain. The R395H substitution was noted in two strains. (D) Reactivity of mAb (#20) to MERS-NP (122–413) derived from the prototype and a mutant strain harboring R395H. Reactivity was determined by immunoblot analysis.
