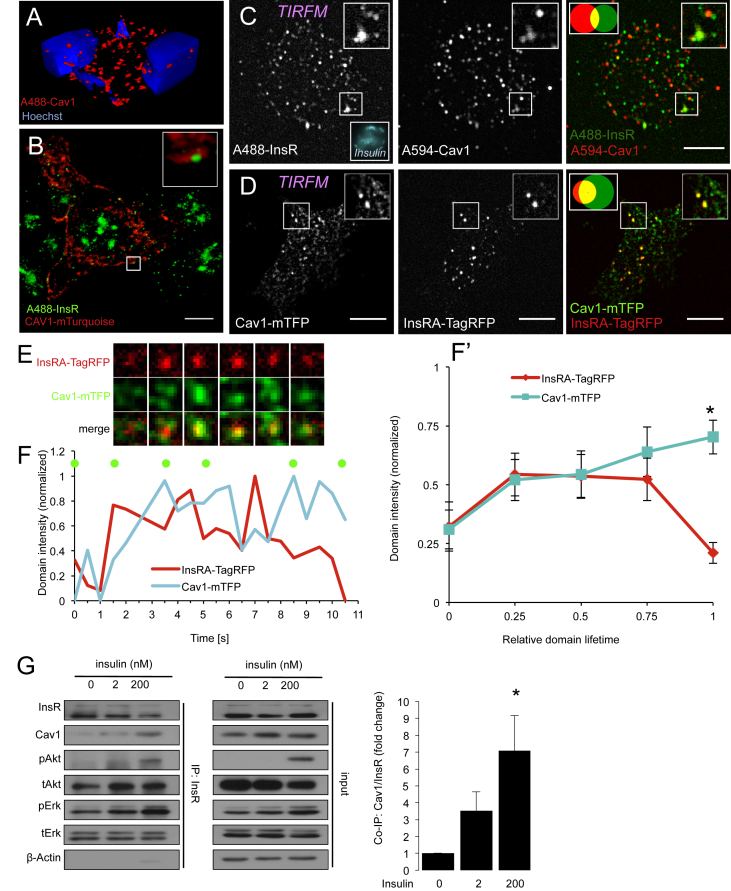
Figure 3.
Caveolin-1 is associated with insulin receptor internalization. (A) 3D reconstruction of subcellular Cav1 staining in murine islets cells of a pancreatic section. (B) STED super-resolution imaging of mTurquoise-tagged Cav1 and endogenous insulin in MIN6 cells. Inset shows Cav1 surrounding a cluster of insulin receptors. Scale bar = 5 μm. (C) Immunolabeling and TIRF microscopy of dispersed human islet cells cultured in 5 mM glucose demonstrates colocalization of endogenous Cav1 to endogenous insulin receptors at the plasma membrane (n = 20 cells). Scale bar = 5 μm. (D) TIRF imaging reveals a high degree of colocalization of Cav1-mTFP to InsRA-TagRFP at the plasma membrane of live MIN6 cells cultured in 20 mM glucose (n = 10). Scale bar = 5 μm. (E, F) Live-cell TIRF imaging in MIN6 cells cultured in 20 mM glucose reveals the reciprocal recruitment of InsRA-TagRFP and Cav1-mTFP to membrane domains prior to the internalization of insulin receptors. Pixel size = 0.129 μm (F, F′) Intensity analysis of a single (F) InsRA-TagRFP positive membrane domain during the process of Cav1 mediated vesicle budding. Green dots correspond to the time points of the images in E. (F′) shows the averaged and normalized intensities of 15 analyzed InsRA-TagRFP positive membrane domains during Cav1 mediated vesicle budding from the plasma membrane of MIN6 cells cultured in 20 mM glucose. *p < 0.05. (G) Co-immunoprecipitation of insulin receptors from NIH-3T3 cells reveals an insulin dependent binding of Cav1 to the insulin receptor (n = 3). NIH-3T3 cells were cultured in 0 mM glucose during insulin treatments for 5 min *p < 0.05