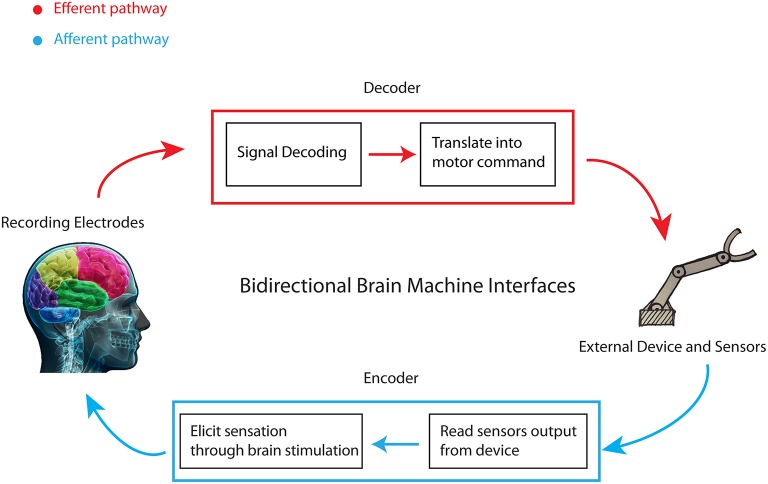
Figure 1.
Schematic of a bidirectional brain-machine interface. A bidirectional BMI has two pathways of communication with the brain: an afferent pathway from some sensors to the brain and an efferent pathway from the brain to a device controlled by it. The decoder—or motor interface—transforms the recorded activity into motor commands for the device. The encoder—or sensory interface—transmits the information about the external world or about the state of the device to the brain by delivering electrical stimulation patterns to it.