Figure 1. Drosophila Fgn Knockdown Increases Synaptic Connections In Vivo.
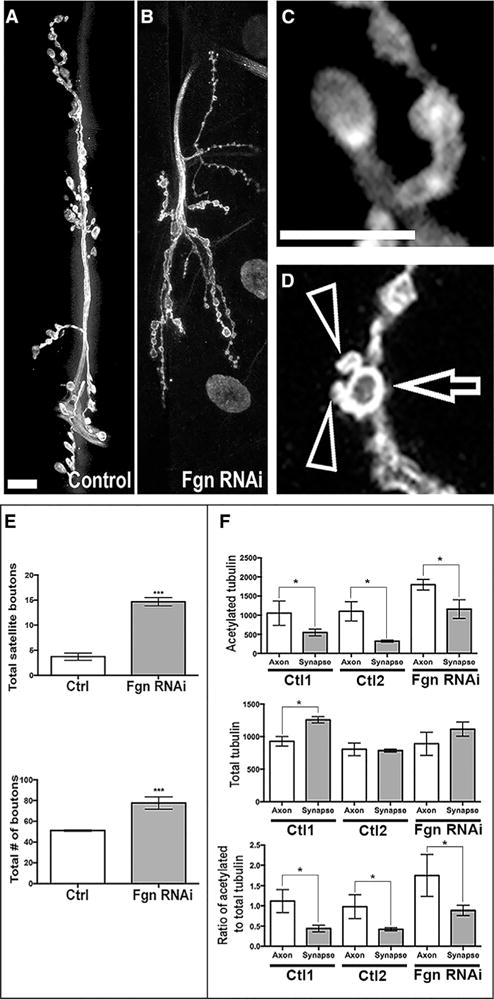
(A–D) Confocal images of third instar larval NMJs, muscles 6 and 7, labeled with α-HRP (white) to detect presynaptic neuronal membranes. The following are shown: (A) a Ctl NMJ; (B) an NMJ from an Fgn-knockdown animal (Dcr2;UAS:Fgn-RNAi;elav-Gal4; note the significant increase in bouton number in Fgn-knockdown animals compared to Ctls); (C) a representative individual bouton from Ctl animals; (D) a bouton with associated satellite boutons from an Fgn-knockdown animal. Arrows show the bouton; arrowheads show satellites. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(E) Quantification of the number of total boutons and satellite boutons in Fgn-knockdown animals compared to Ctls is shown.
(F) Quantification of IF intensity of acetylated tubulin (top), total tubulin (middle), and ratio of acetylated to total tubulin (bottom) between Fgn-knockdown animals (Dcr2;UAS:Fgn-RNAi;elav-Gal4) and outcrossed Ctls (Dcr2;;elav-Gal4 and UAS:Fgn-RNAi/+) at both the axonal shaft and distal synapse near the bouton. Note the significant increase of the ratio of acetylated tubulin to total tubulin. Error bars represent SE. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
