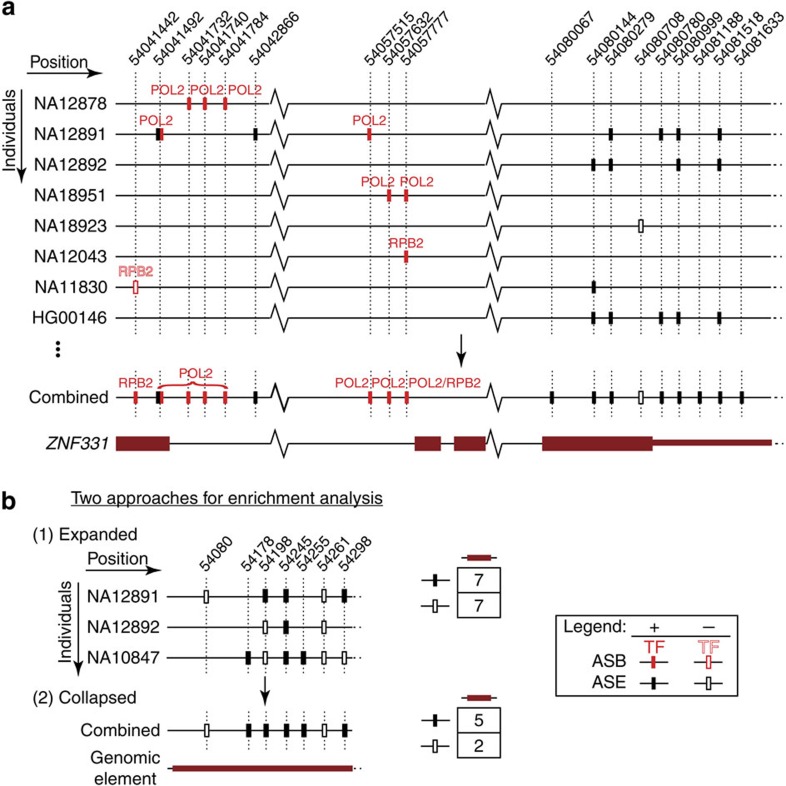
Figure 3. Part of the ZNF331 gene on chromosome 19, position 54,041,442-54,081,633 (hg19).
(a) ASB and ASE SNVs in allele-specific gene ZNF331. From AlleleDB, we can observe the ASB SNVs (filled red bars with the name of the TF above the bars) and ASE SNVs (filled black bars) found in each individual (row) and genomic positions (columns) along the ZNF331 gene. We can see that many of these SNVs are sparsely distributed across a single individual. By collapsing or combining information from multiple individuals, we can identify genomic regions or elements that are enriched for allele-specific activity. Unfilled black and red bars denote control SNVs are heterozygous SNVs that have enough reads to be tested but are non-allele-specific. (b) Two approaches for enrichment analyses are performed for each genomic element. (1) The ‘expanded' enrichment is performed in a population-aware fashion, in which each occurrence of allele-specific or control non-allele-specific SNV in each individual is counted. (2) The ‘collapsed' enrichment conflates all occurrences over multiple individuals into a single unique SNV position as long as an allele-specific or accessible non-allele-specific SNV occurs in at least one individual.