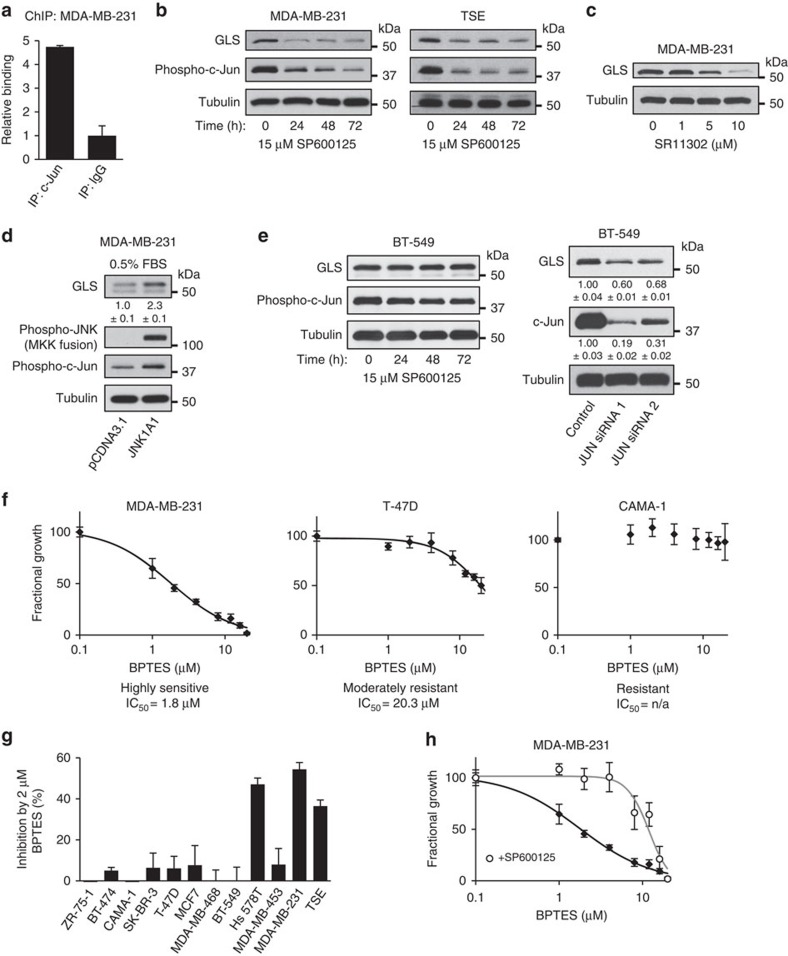
Figure 5. Inhibition of c-Jun suppresses GLS expression and BPTES sensitivity in human breast cancer cell lines.
(a) ChIP analysis showing that c-Jun binds to the GLS promoter. Complexes containing c-Jun were immunoprecipitated from cross-linked, digested, chromatin isolated from MDA-MB-231 cells. A parallel immunoprecipitation using rabbit IgG was carried out as a negative control. Following reversal of cross-links and purification of DNA, RT–PCR was run using primers designed to amplify a 196-bp fragment centred on the putative c-Jun binding site at position −188 bp relative to the TSS. The data presented are the RQ values, with error bars marking RQ max and RQ min, from triplicate reactions. (b) Western blot analysis showing that treatment of MDA-MB-231 or TSE cells with the JNK inhibitor SP600125 (15 μM) leads to decreased phosphorylation of c-Jun, and decreased GLS levels. (c) Treatment of MDA-MB-231 cells with the AP-1 inhibitor SR11302 (1–10 μM) for 48 h results in a dose-dependent decrease in GLS. (d) Western blot analysis showing that transient transfection of MDA-MB-231 cells with a constitutively activated JNK fusion construct results in increased c-Jun phosphorylation and upregulated GLS levels. Cells were collected 48 h after transfection. (e) Western blot analysis showing that in the drug-resistant breast cancer cell line BT-549, treatment with 15 μM SP600125 has little effect on c-Jun phosphorylation and does not lead to decreased GLS levels (left panels). However, knockdown of JUN expression using siRNAs leads to decreased GLS levels. Relative band intensities are indicated. (f) Representative BPTES dose curves showing the effect of BPTES on the proliferation of breast cancer cell lines over 6 days. Curves were fitted using SigmaPlot, with data from triplicate assays. (g) Sensitivity of breast cancer cell lines to GLS inhibition, as indicated by inhibition of proliferation over 6 days by 2 μM BPTES. Of the high-c-Jun lines, only the drug-resistant BT-549 cells were not highly sensitive to BPTES. None of the low-c-Jun lines were highly sensitive. Data presented are the mean±s.d. of triplicate assays. (h) BPTES dose curves for MDA-MB-231 cells±15 μM SP600125, showing that inhibition of JNK desensitizes cells to GLS inhibition (the IC50 for BPTES shifts from 1.8 to 12 μM). Curves were fitted using SigmaPlot, with data from triplicate assays. Relative densitometry data are the mean±s.d. of triplicate blots.