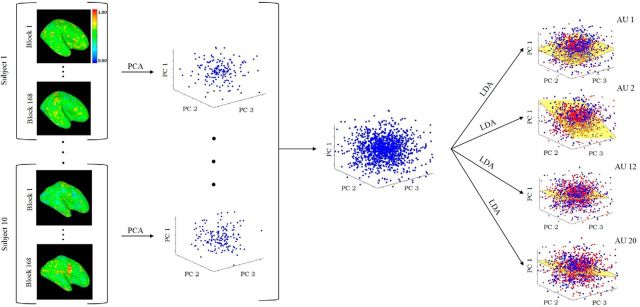
Figure 2.
Subjects observed images of facial expressions with AU 1, AU 2, AU 12, and AU 20 either present or not present. Images were shown in blocks of six images each. Subjects saw a total of 168 blocks. The fMRI BOLD responses (see Materials and Methods) for each of these blocks are shown on the left column. The 168 responses of each subject are used to compute the covariance matrix (ΣX) of the data, from which the PCs are obtained (middle column). This yields a common PCA feature representation for all subjects. Classification of each AU (present versus not present) is computed in this common PCA space. LDA is used as a classifier. Each LDA (i.e., to determine the presence of each AU) is a hyperplane dividing the PCA space into two regions: one region corresponds to the samples with that specific AU present and the other region to samples of this AU not present (right-most column). This figure illustrates the approach as it applies to a whole-brain analysis. When studying the hypothesis that the computations of visual recognition of AUs is in the pSTS, only those voxels in the pSTS region were used.