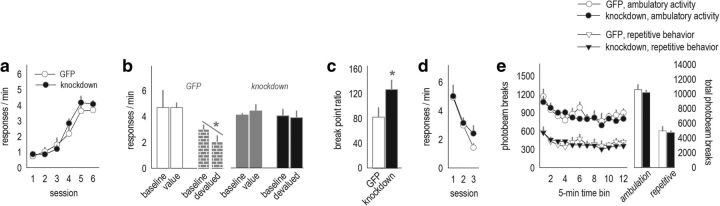
Figure 2.
Selective Bdnf knockdown in the mOFC decreases behavioral sensitivity to reinforcer value and PR response requirements. a, Cre-expressing viral vectors were infused into the mOFC (as in Fig. 1d) of “floxed” Bdnf mice. Mice were trained to nose poke for food reinforcers, with no differences between groups. b, After prefeeding devaluation (and in the absence of an injection stressor as in Fig. 1), control GFP-expressing mice decreased response rates relative to baseline. Meanwhile, selective Bdnf knockdown mice failed to modify response rates. Instead, response rates were indistinguishable from those generated by mice that had access to regular chow before test (value groups). c, mOFC Bdnf knockdown also increased breakpoint ratios. d, Meanwhile, response extinction was not affected; e, furthermore, spontaneous locomotor activity was unaffected. Ambulatory and repetitive photobeam breaks are represented in 5 min bins (left) and 1 h total counts (right). Symbols represent means ± SEMs. *p < 0.05. n = 8 per group.