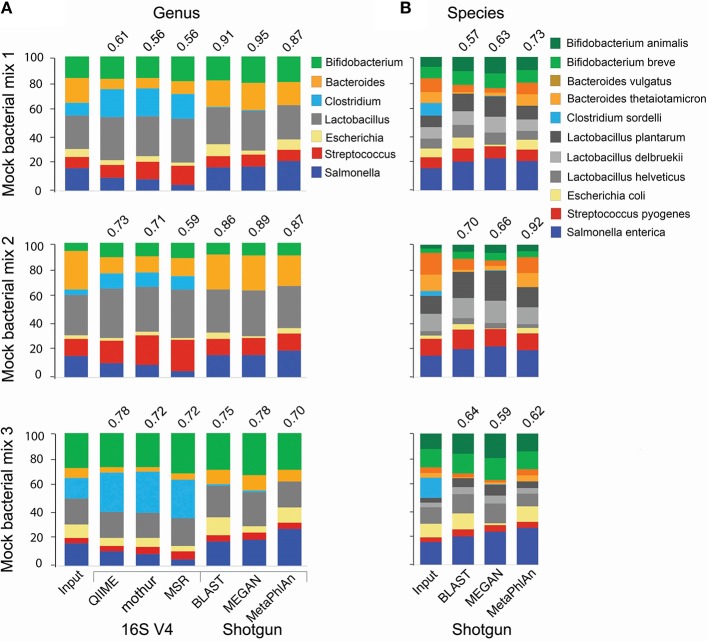
Figure 1.
Comparison of taxonomic analyses of a low complexity artificial microbial population using 16S amplicon or shotgun metagenomic approaches. Eleven bacterial species (representing 7 genera) were cultured under standard laboratory conditions. DNA was extracted using the FastDNA spin kit for feces (MPBio). 16S amplicon and shotgun metagenomics libraries were constructed using the NEXTflex 16S V4 Amplicon-Seq (BioO Scientific) and the Nextera XT (Illumina) kits, respectively. Libraries were paired-end sequenced on a MiSeq sequencer using a 500-cycle kit. For 16S libraries, sequences were trimmed with the “split_fastq_libraries.py” script from QIIME. Default parameters were used, with the exception that the quality threshold for trimming was raised to 30. PCR primer sequences were trimmed with in-house Perl scripts. Shotgun metagenomics libraries were trimmed with the fastqMcf tool, and a quality threshold of 15. The relative abundance of each species was determined with the software indicated at the bottom of the bar graph, using default parameters, at the genus (A) or species (B) levels. The Pearson correlation coefficient between the expected (Input) relative abundance and the classification performed by each program is indicated on top of the bar graph.