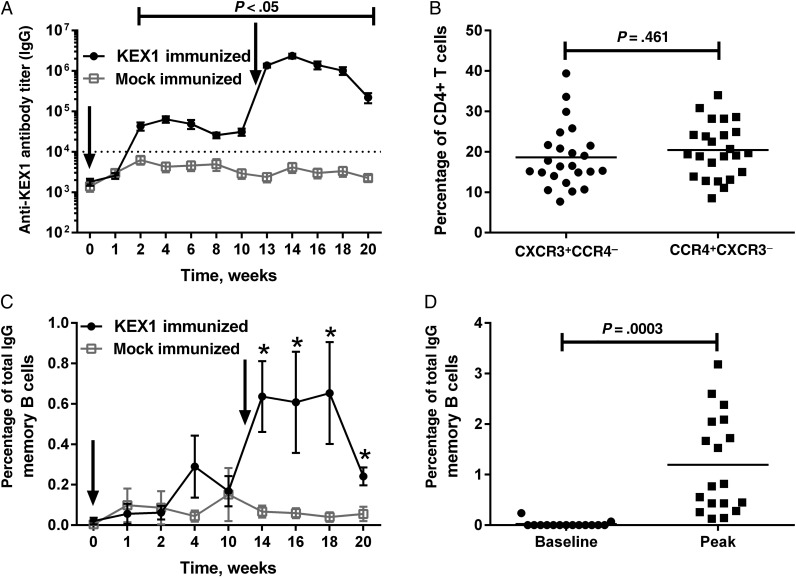
Figure 1.
KEX1-specific humoral immune responses following immunization and boost with KEX1/alum in normal macaques. A, Mean plasma KEX1-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) titer, as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Dashed line indicates KEX1-specific IgG titer correlate of protection. Arrows indicate time of immunizations. B, To evaluate skewing of T-helper cell phenotype, peripheral blood lymphocytes were analyzed by flow cytometry for surface markers associated with either T-helper type 1 (Th1; CXCR3+CCR4−) or T-helper type 2 (Th2; CCR4+CXCR3−) CD4+ T cells and expressed as a percentage of total peripheral blood CD4+ T cells. The frequency of peripheral blood CD4+ Th1 and Th2 cells at the time of SHIV-infection was similar (P = .461). C, Kinetics of KEX1-specific memory B-cell responses, determined by B-cell enzyme-linked immunospot analysis and expressed as the mean percentage of total IgG B cells. D, Comparison of peak KEX1-specific memory B cells to baseline data (KEX1-immunized animals only). Paired Student t tests or Wilcoxon signed rank tests were performed to compare data baseline to data at indicated time points. *P < .05, compared with baseline.