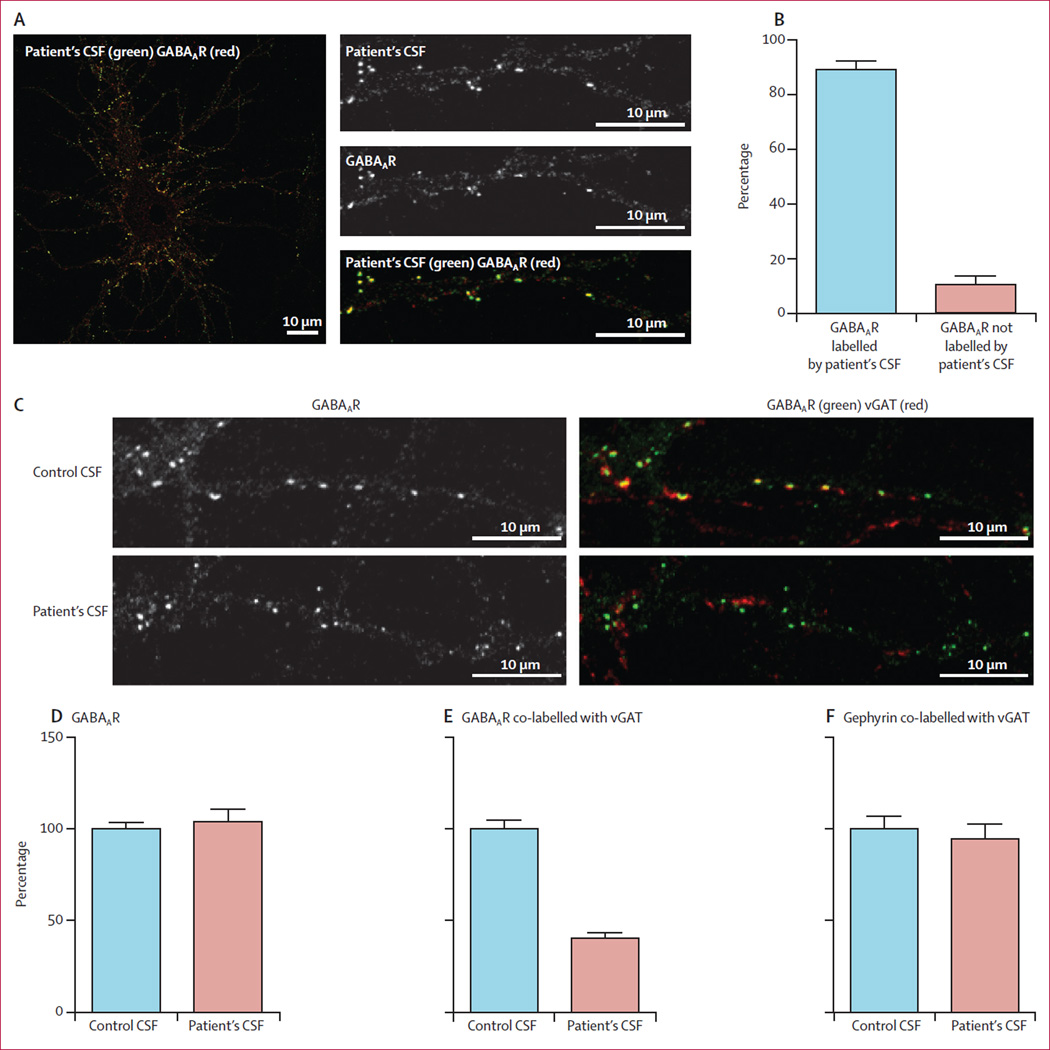
Figure 6. Effect of patient’s antibodies on the density of GABAAR clusters in cultures of hippocampal neurons.
Live 14-day-in-vitro cultures of dissociated rat hippocampal neurons were stained with patient’s CSF containing GABAAR antibodies (green), then fixed and stained with commercial GABAAR antibodies (red; A). Quantification of colocalisation between patient’s CSF antibodies and the commercial GABAAR antibody shows that 89% (SE 3%) of receptors labelled by patient’s antibodies were colabelled with the commercial antibody against GABAAR (B). In a similar assay, neurons were incubated with patient’s CSF for 48 h and subsequently stained for postsynaptic GABAAR (green) and presynaptic vesicular GABA transporter (vGAT) (red; C). The synaptic GABAARs (shown as yellow clusters in control conditions) were greatly reduced after treatment with patient’s CSF (C). The number of GABAAR clusters along dendrites of neurons treated with patient’s CSF is not different from neurons treated with control CSF (Mann-Whitney test p=0·6; D). The number of GABAARs localised in synapses, however, decreased significantly in neurons treated with a patient’s CSF compared with neurons treated with control CSF (40% [3%] compared with control as 100%; p<0·0001; E). Patients’ CSF did not affect the clusters of post-synaptic gephyrin colabelled with presynaptic vGAT when compared with the effects of control CSF (p=0·5; F).