Fig 1. The HPOL signaling network in rainbow trout as formulated in our model.
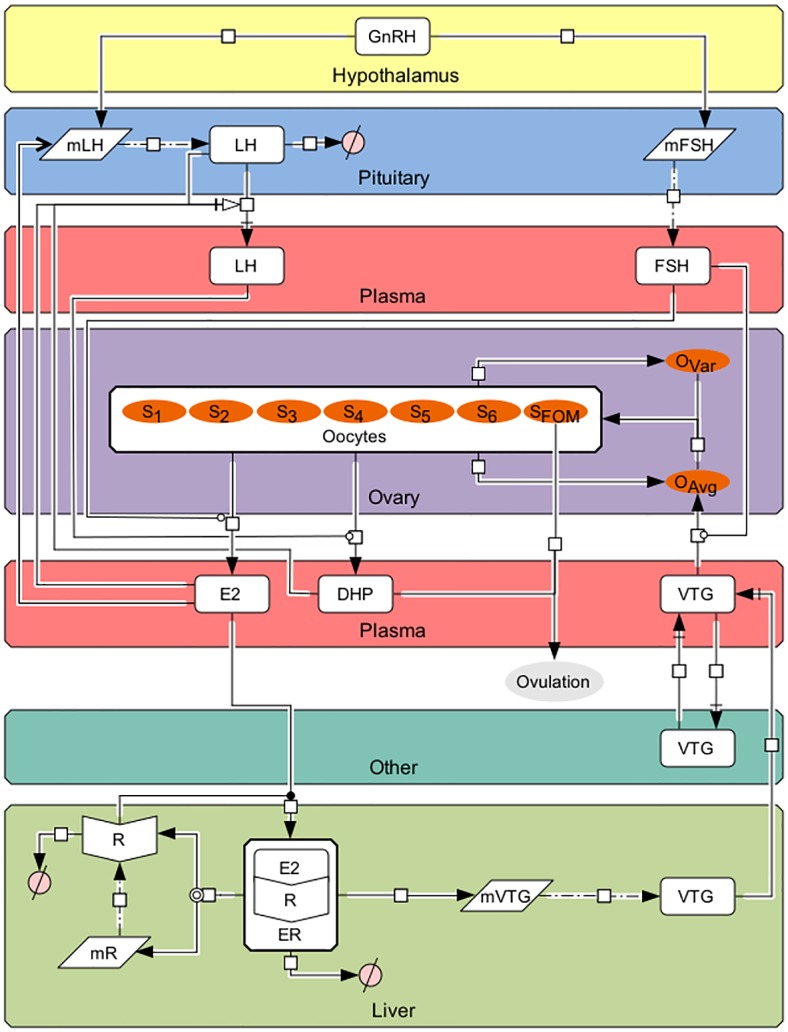
Arrows and symbols on graph follow CellDesigner vs. 4.4 notation (www.celldesigner.org). GnRH is secreted from the hypothalamus into the pituitary stimulating the production of mFSH and mLH, which then leads to formation of FSH and LH, respectively. FSH, which is being continuously secreted from the pituitary, travels to the ovaries to stimulate production of E2. E2 then travels to the liver to bind with E2 receptors (R; translated from mR) to form ER. ER then stimulates the production of mVTG, which produces VTGL. Secreted VTG then travels from the liver to the ovaries via the plasma (VTGP) where it is absorbed by follicles in stages 3 through 6 (the proportion of follicles in these stages are denoted by Sj, j = 3, 4, 5, and 6) during vitellogenesis, the rate of which is affected by FSHP, to promote oocyte growth (OAvg). Oocyte growth then progresses the oocytes through the stages using a Weibull distribution created from OAvg together with OVar. In the later stages LHP stimulates the oocytes to produce DHP. Finally, oocytes undergo final maturation (SFOM) and combined with DHP, determine when the fish ovulates. Description of symbols are found in Table 1.
