Figure 1.
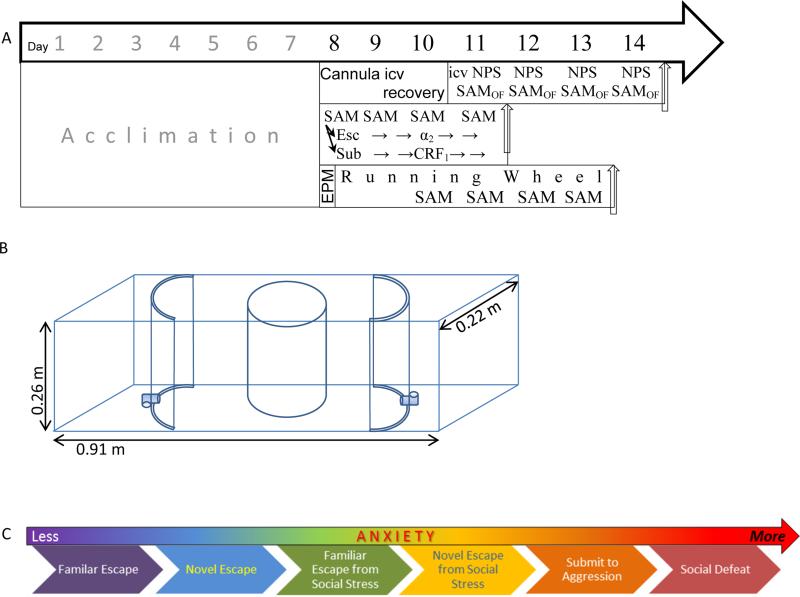
A) Timelines of the experimental protocols all begin with seven days of acclimation to cages, followed thereafter by anxiogenic or anxiolytic treatments. Interaction with SAM apparatus occurred over four days, and may have taken place in the presence (middle and bottom timelines) or absence (top) of a larger conspecific aggressor. Top) For experiments in which the anxiolytic Neuropeptide S (NPS) is delivered icv, intraventricular cannula placement was executed on day eight followed by recover until icv injection of NPS and interaction with the empty SAM apparatus of each of days eleven through fourteen to test for open field (OF) anxious behavior and escape. Middle) Social anxiety and escape was tested by ip injection of the know anxiogenic α2-adrenoreceptor antagonist yohimbine in escaping animals (determined on days 1 and 2 of SAM interaction; days 8 and 9 overall) or the anxiolytic CRF1 antagonist antalarmin in submitting animals, just prior to day 3 and measuring latency to escape or inhibition of escape on days 3 and 4 of SAM social interactions (days 10 and 11 overall). Bottom) For the voluntary exercise experiments, mice were tested for predisposition for anxious behavior on the EPM on day 8 and then provided a running wheel for 6 days. Social interactions in the SAM begin after 2 days of running, and continue for another 4 days (days 10 – 13 overall). The icv NPS experiment ended on day 14, the yohimbine/antalarmin experiments on day 11, and the running wheel experiments ended on day 13. B) The SAM apparatus includes an open field (OF) arena that can be adjusted for size. The OF includes two escape routes, which lead to safe zones only accessible to small test mice. Test mice are added within the opaque cylindrical divider. Large aggressors are added outside the cylindrical divider. The divider is removed to allow social interaction. C) The continuum or gradient of intensity of anxious behavior as revealed by the Stress-Alternatives Model.