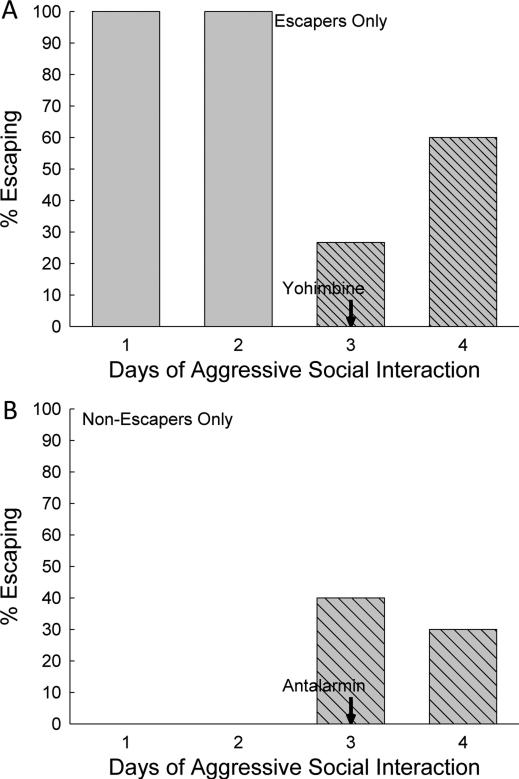
Figure 2.
Anxiogenic (A) and Anxiolytic (B) drug treatments on day 3 of SAM exposure changed escaping (A) or submissive (B) behavioral phenotypes in a substantial proportion of socially interactive mice. A) The anxiogenic α2-adrenoreceptor antagonist yohimbine inhibited escape behavior. Prior to ip delivery of yohimbine, all of the mice that would receive the anxiogenic drug escaped (light gray wide hatched bars; escaping animals were chosen for this treatment), but on the day of yohimbine administration only approximately one fourth of the animals escaped (dark gray bars with narrow hatching), and over 70% remained submissively. On the following day (4), with no additional α2-adrenoreceptor inhibition, most (60%) returned to escape behavior, with 40% continuing to remain submissively. B) The anxiolytic CRF1 receptor antagonist antalarmin promoted escape behavior in previously non-escaping submissive mice. Prior to ip delivery of antalarmin, none of the mice that would receive the anxiolytic drug escaped (no bars are evident; submissive animals were chosen for this treatment), but on the day of antalarmin administration 40% of the animals escaped (cross hatched bars). On day 4 (no drug treatment) 30% continued to escape.