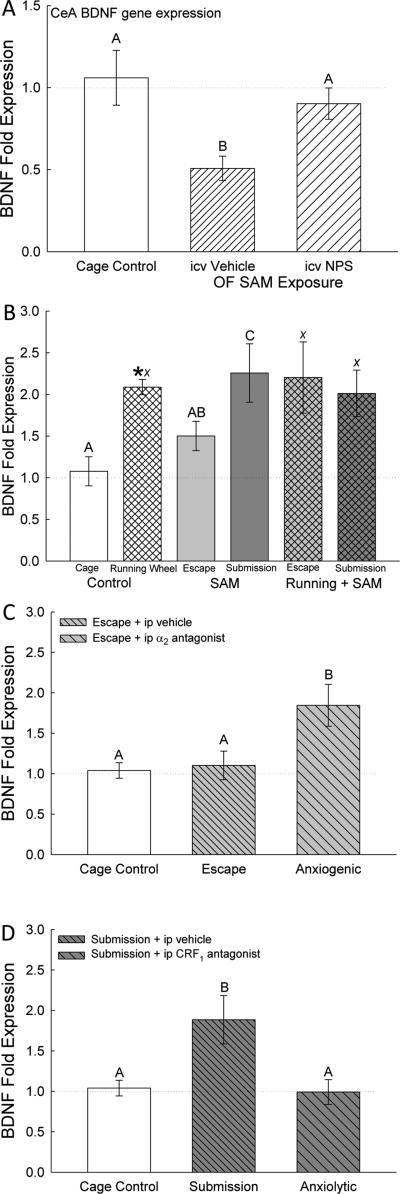
Figure 6.
Intra-amygdalar (central amygdala, CeA) brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene expression (mean ± SEM) is elevated by anxiogenic/stressful conditions, and alleviated by anxiolytic conditions. There were no effects of treatments on BDNF TrKB receptor mRNA. A) Injection (icv) of NPS (cross hatched bars) returned BDNF mRNA in CeA to cage control expression levels (clear bars), compared to reduced expression in icv aCSF (vehicle) injection (hatched bar). B) Running wheels (*) and submission increased BDNF fold expression in the CeA, compared with cage controls (clear bars) and escaping mice without exercise (hatched bars). C) Increased CeA BDNF mRNA in submissive animals (similar to B; cross hatched bars) is ameliorated by anxiolytic CRF1 antagonist antalarmin treatment (gray bars). D) The anxiogenic α2-adrenoreceptor antagonist yohimbine stimulated increased BDNF gene expression in the CeA, compared to cage controls (clear bar) and escaping mice (hatched bar). Bars marked with differing letters above the mean/error bar (e.g. A, B, C; or X and Y) are significantly different, whereas bars marked with the same letter (such as A and AB) are not significantly different.