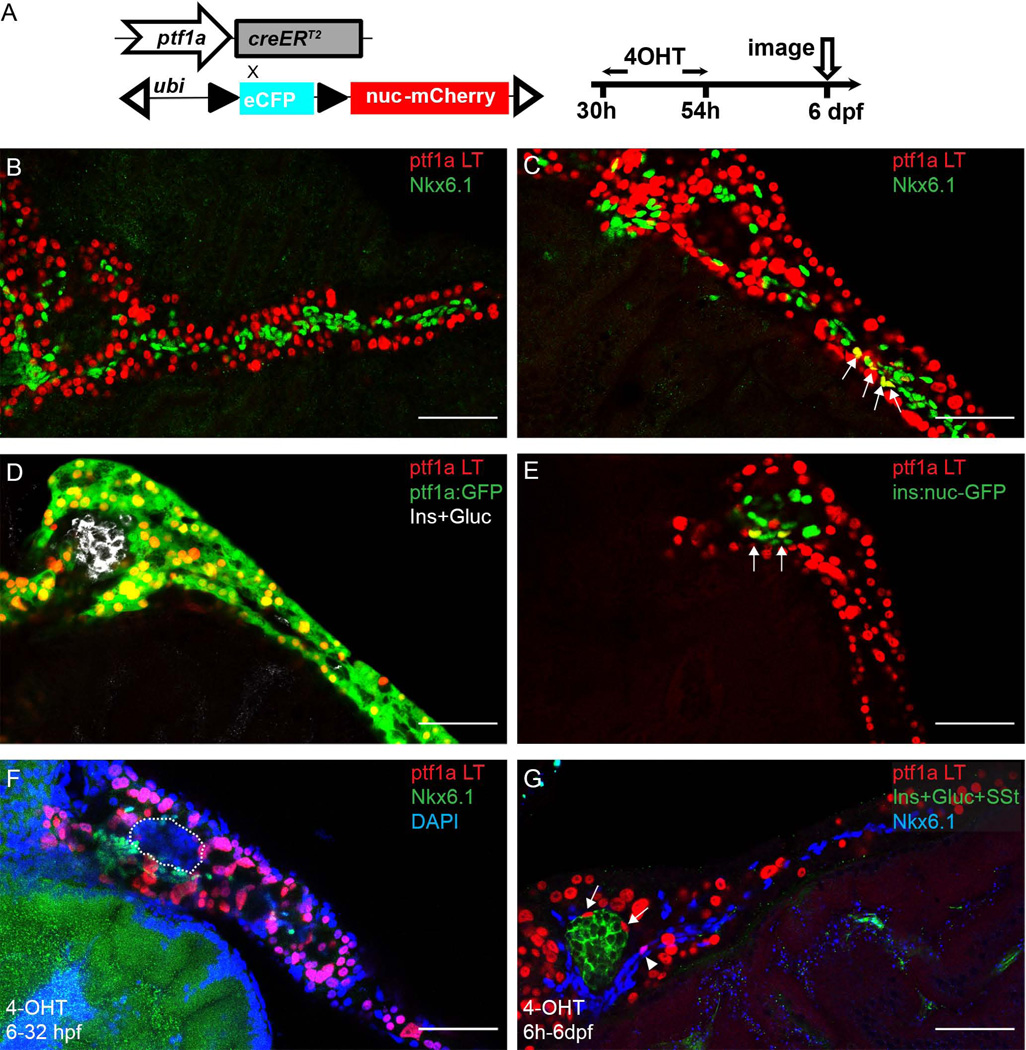
Figure 2. The early ptf1a lineage generates a small fraction of PNC and endocrine cells.
(A) Experimental setup. (B–G) In all the panels, ptf1a lineage is indicated by nuclear-mCherry expression (red). (B, C) Immunofluorescence for Nkx6.1 (green) labels PNCs. (B) In some pancreata, the ptf1a lineage and PNCs show no overlap. (C) In some pancreata, ptf1a-lineage labeled cells are traced into PNCs. Arrows point to colabeling events. (D) In some pancreata, the ptf1a lineage has no demonstrable contribution to endocrine cell types. ptf1a:GFP transgene (green) shows current expression of ptf1a, which, at 6 dpf, is limited to acinar cells. Endocrine cells are labeled by a mixture of antibodies against Insulin (Ins) and Glucagon (Gluc), white. (E) In a few pancreata, some of the cells derived from the ptf1a lineage are co-labelled by the ins:nuc-GFP transgene (green), which is visualized in the nuclei of Insulin-secreting cells. Arrows point to co-labeling events. (F) 4-OHT treatment at 6h-32hpf. In the pancreas shown, there are no ptf1a lineage-labeled cells observed in the endocrine compartment (outlined) nor PNCs (Nkx6.1, green). (G) 4-OHT treatment at 6h-6dpf. Nkx6.1, blue. Arrows point to ptf1a lineage-labeled endocrine cells. Arrowhead points to ptf1a lineage-labeled PNCs. Scale bar, 50 µm.