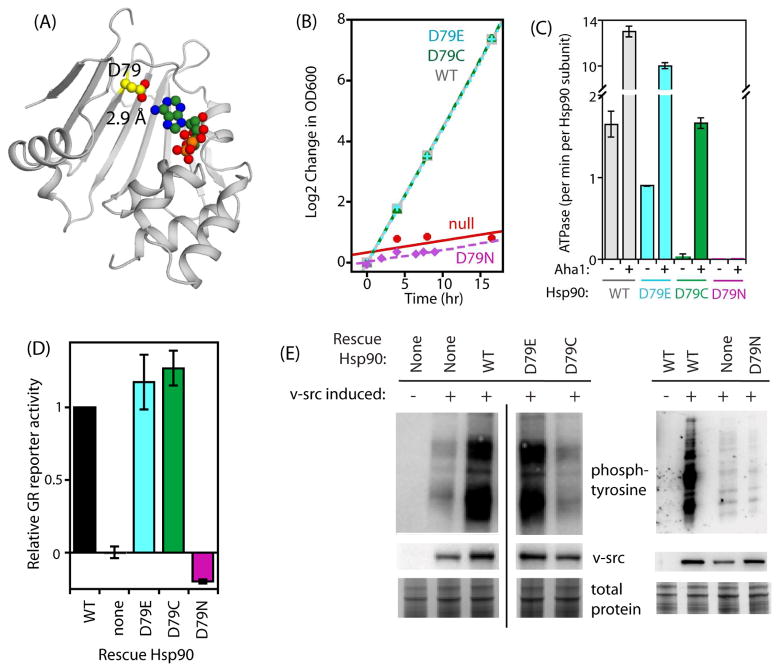
Figure 4. Contacts between D79 and adenine can be altered without compromising Hsp90 function.
(A) Structural representation of the N-domain of Hsp90 highlighting the near ideal geometry of the hydrogen bond formed between N6 of adenine and the side chain of D79. (B) Growth rate of budding yeast in monoculture for D79E, D79C, and D79N Hsp90 variants. (C) ATPase rates observed for purified Hsp90 proteins (2.5 μM) in the presence and absence of the co-chaperone Aha1 (10 μM). (D) Ability of D79E, D79C and D79N Hsp90 to mature the GR client in yeast. (E) Efficiency of v-src maturation supported by D79E, D79C, and D79N Hsp90 variants. The black vertical line indicates where lanes were removed for figure clarity. D79N along with appropriate controls were analyzed on a separate blot that is shown on the right side of this panel. See also Figure S5.