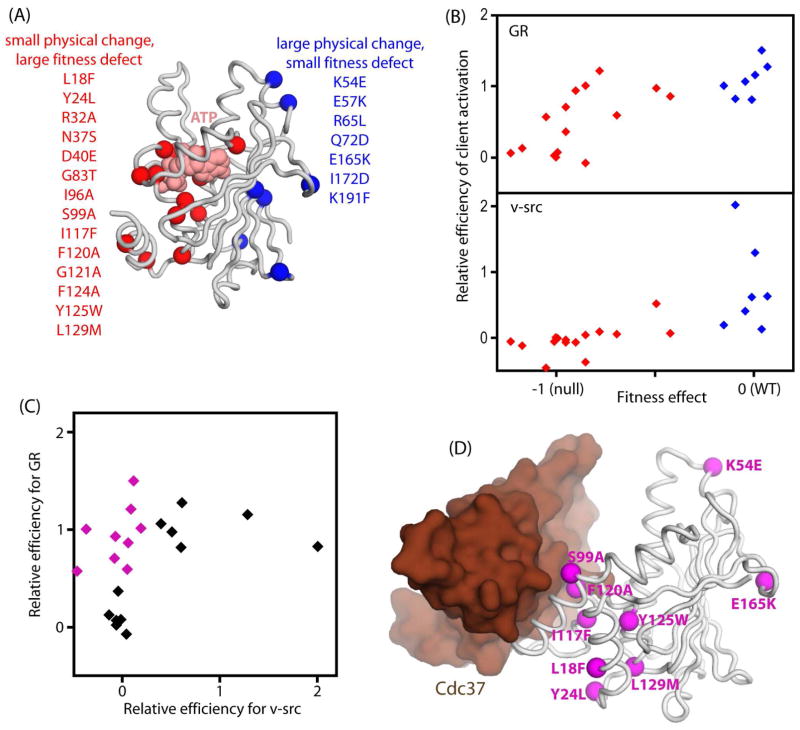
Figure 5. Identification of Hsp90 mutants that differentially impact the maturation of GR and v-src.
(A) Structural representation of the N-domain of Hsp90 indicating mutations identified as having a strong potential for separation of function. (B) The effects of individually cloned Hsp90 variants on activation of GR and v-src compared to effects on yeast growth rate. (C) Comparison of the effects of Hsp90 mutants on activation efficiency for GR versus v-src identifies eight mutations with severe deficiency for v-src that are capable of mediating the efficient activation of GR. (D) Structural representation of the N-domain of Hsp90 and the Cdc37 co-chaperone based on 1US7.PDB (Roe et al., 2004) indicating the location of the sites of mutations that caused client-specific effects. See also Figure S6.