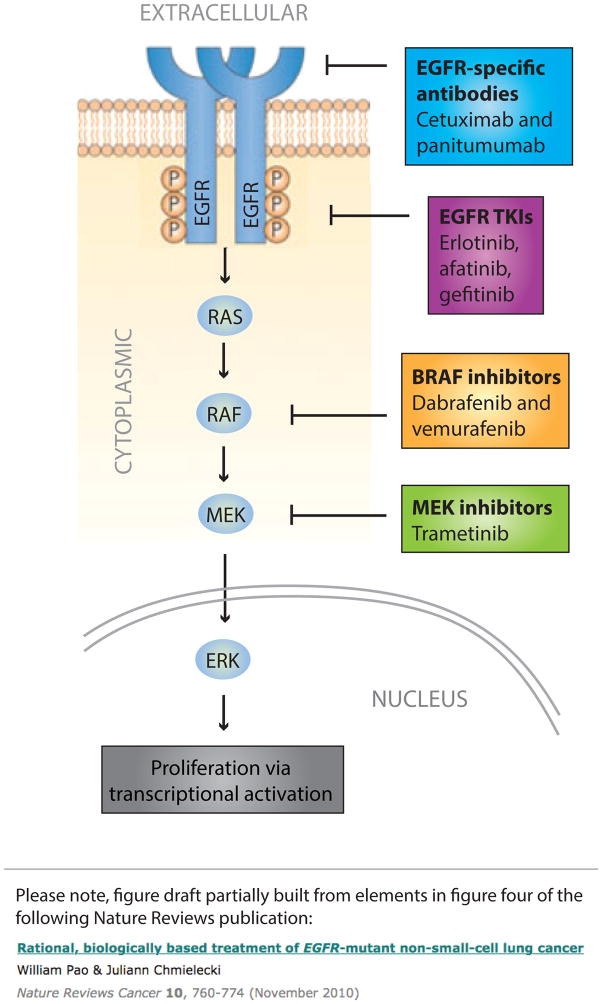
Figure 2.
Core elements of the human EGFR–MAPK pathway. The schematic representation shows the EGFR receptor tyrosine kinase and the MAPK signalling cascade activated downstream of this receptor. The current FDA-approved molecularly targeted agents with indications that are determined by a companion molecular diagnostic assay are shown at their main point of activity. The presence of particular mutations assessed using the companion diagnostic tests can determine whether the patient is eligible or ineligible for therapy, depending on the setting. RAS mutations, for example, rule out the use of EGFR monoclonal antibodies in patients with colorectal cancer. By contrast, the presence of activating mutations in EGFR (such as deletions in exon 19 or the single-nucleotide polymorphisms that result in the Leu858Arg mutation) indicate eligibility of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer for treatment with small-molecule TKIs of EGFR. Similarly, activating Val600 mutations in BRAF confer sensitivity, rather than resistance to BRAF and/or MEK inhibitors. Abbreviations: EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; TKIs, tyrosine-kinase inhibitors.