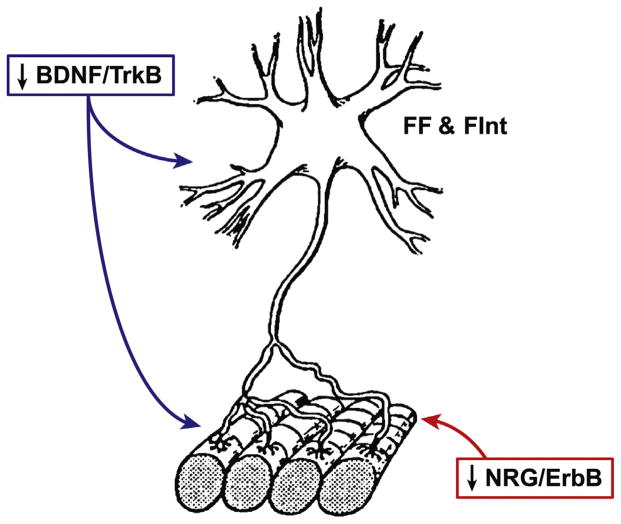
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustrating a fast-twitch fatigable (type FF) and fast-twitch fatigue intermediate (type FInt) motor unit. Muscle fibers corresponding to type FF and FInt motor units are most susceptible to atrophy and weakness secondary to the natural aging process and denervation. Two neurotrophic factors that may be mediating this fiber type specific effect of atrophy and weakness are: (1) brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) acting through the tropomyosin-related kinase receptor B (TrkB) which is involved in motor neuron survival, excitability, and neuromuscular synaptic transmission, and (2) the trophic factor family of neuregulins (NRG) which activate tyrosine kinases of the ErbB receptor family that is released from the motor neuron exerting an anabolic effect on muscle fibers and is implicated in the matching of motor neuron to muscle fiber properties.