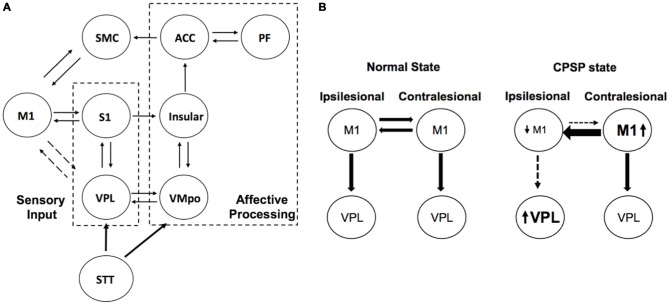
Figure 1.
Schema explaining interhemispheric inhibition (IHI) in central post-stroke pain (CPSP). (A) Simplified pain circuit model composed of lateral and medial thalamic pain pathways. The motor cortex (M1)-VPL connection is described as dotted lines as there is an indirect connection. It should be also noted that there is an indirect somatosensory projection from the S1 to insular cortex through posterior parietal cortex (Price, 2000). (B) Impaired descending inhibition pathways from primary M1. Ipsilesional M1 activity is decreased due to not only stroke lesion but also inhibitory signals from the contralateral M1. ACC, anterior cingulate cortex; PF, prefrontal; SMC, supplementary motor cortex; STT, spinothalamic tract; VMPo, posterior ventromedial nucleus of the thalamus; VPL, ventral posterolateral nucleus of the thalamus.