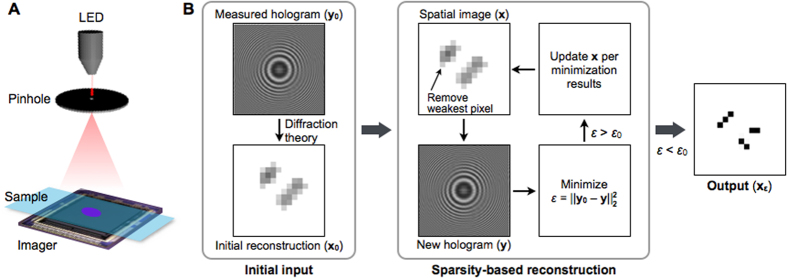
Figure 1. Sparsity-based algorithm to enhance the spatial resolution in lens-free digital inline holography (LDIH).
(A) Imaging schematic of a typical LDIH system. The system consists of a light-emitting diode (LED), a pinhole, and an imager. A sample is placed directly above the imager, and the hologram coming from the sample is recorded. (B) Block diagram of the developed algorithm. The measured hologram (y0) and its numerical reconstruction (x0) via diffraction theory are used as an initial input. The sparsity-based routine executes an iterative minimization. In each iteration, the algorithm first increases the sparsity of the spatial image (x) by removing the weakest pixel and generates a new hologram (y). The algorithm then minimizes the difference (ε) between y and y0 by adjusting the pixel values of the spatial image at a given sparsity. The combination of pixel values that produces smallest ε is selected to update x. The iteration stops when ε becomes smaller than the threshold value ε0, and the final output (xε) is obtained.