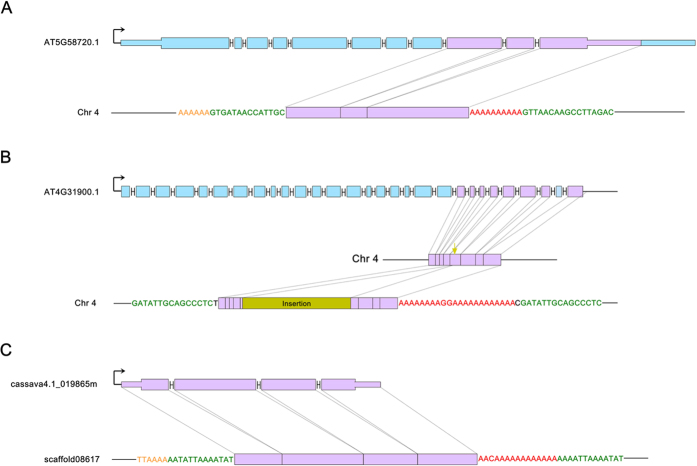
Figure 1. Schematic representation of three retrocopies.
Thick and thin boxes stand for the coding region and the untranslated region, respectively. The symbol like “H” refers to intron. The exon size is roughly drawn to scale. The arrow means the transcription direction. The dashed line shows the correspondance of sequences between the parental gene and the retroCNV. The retroposed segment is marked in purple with the other in light blue. For the retroCNV, the candidate target site, target site duplication and polyA tail are marked in orange, green, and red, respectively. Panel (A) shows the retroCNV derived from the parental gene AT5G58720.1 in Arabidopsis where a partial sequence derived from the last three exons of AT5G58720.1 was retroposed and inserted into Chromosome 4 (Chr 4). Panel (B) shows a retrocopy encoded by the Arabidopsis reference genome, and Panel (C) shows a retrocopy encoded by the M. esculenta reference genome. Interestingly, in Panel (B), an insertion of LTR retrotransposon (Copia) occurrs in the middle of the retrocopy, which is marked in dark yellow.