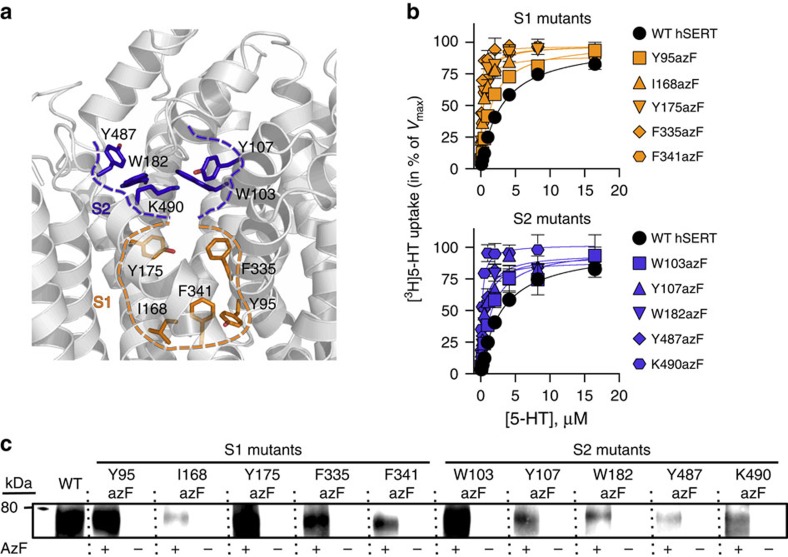
Figure 2. Characterization of hSERT containing photocrosslinking UAAs around the S1- and S2-binding sites.
(a) Homology model of hSERT showing the residues in the S1- and S2-binding sites that were mutated to azF. Residues located within the S1 and S2 sites are shown in orange and purple, respectively. (b) [3H]5-HT uptake saturation curves (normalized to the maximal rate of transport, Vmax) in HEK293T cells expressing WT hSERT and the five S1 azF mutants (orange symbols) or the five S2 azF mutants (purple symbols), illustrating the effects of the azF mutations on the uptake kinetics of the transporter (see Supplementary Table 3 for Km and Vmax values). Data points are represented as mean±s.e.m. from a representative experiment with triplicate determinations. (c) Immunoblot analysis of lysates from HEK293T cells expressing WT hSERT or azF mutants, using a mAb against a C-terminal 1D4 epitope fused to hSERT. Using an epitope at the C terminus of the transporter, only full-length protein is detected in the immunoblot analysis. Cells were grown either in the presence or absence of azF. For the azF mutants, no full-length protein was detected in the absence of azF, illustrating that translation stopped when the amber stop codon was reached.