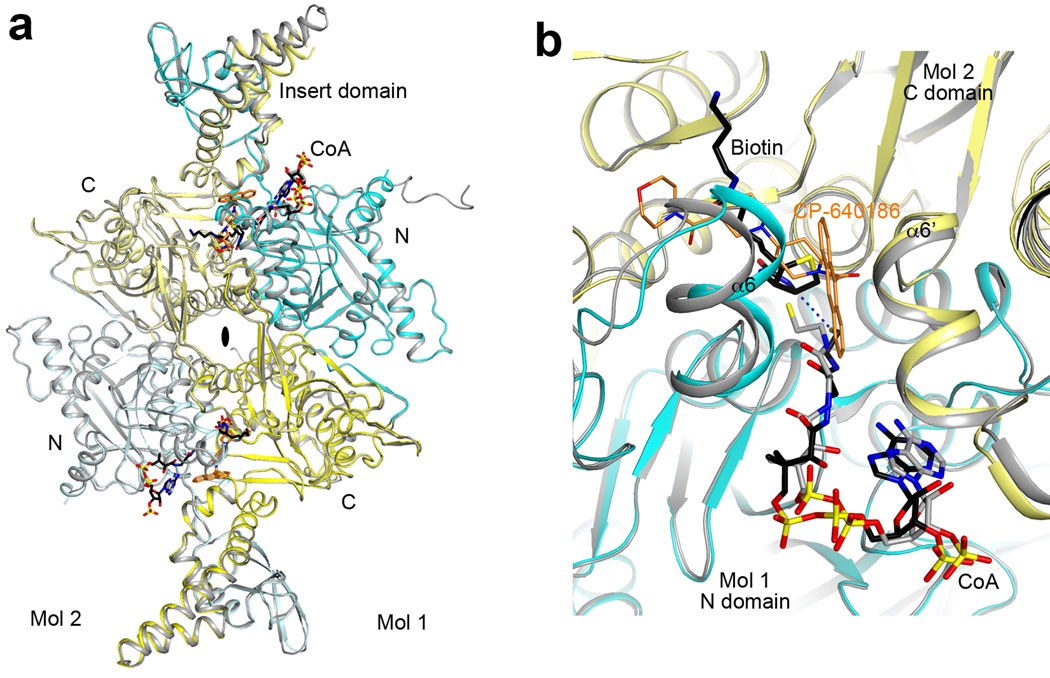
Extended Data Fig. 8.
Structure of the CT domain dimer of ScACC. (a). Overlay of the CT domain dimer in the ScACC holoenzyme (cyan and yellow for N and C domains of protomer 1, light cyan and light yellow for protomer 2) in complex with CoA (black) with the CT domain alone in complex with CoA (gray). Biotin is shown in black and BCCP is omitted for clarity. The bound position of the CP-640186 inhibitor (gold) is shown for reference. A conformational change for the insert domain at the top is due to the binding of BCCP in the holoenzyme, while the insert domain at the bottom shows essentially no change because the BCCP-biotin is not bound as deeply into this active site. (b). Overlay of the CT active site (cyan and yellow) of ScACC holoenzyme with that of CT alone in complex with CoA (gray). The CP-640186 inhibitor (gold) clashes with the bound position of biotin (black). The thiol group of CoA in the holoenzyme complex is 4.3 Å from the N1 atom of biotin (dashed line in blue). The thiol group of CoA in the CT domain alone complex is in a different position, likely due to the absence of biotin in the active site.