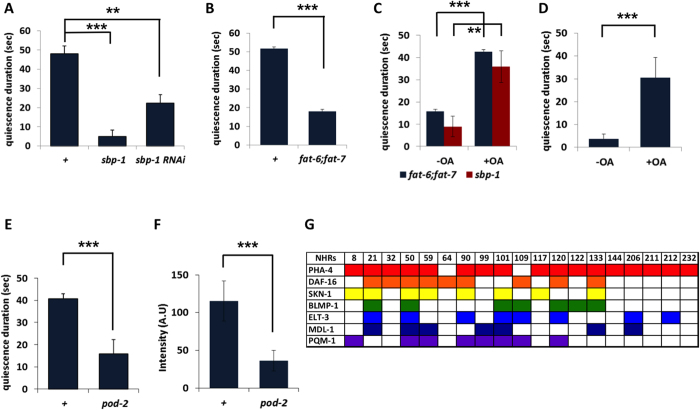
Figure 1. Fat is necessary for satiety quiescence.
(A–D) Satiety quiescence depends on fat storage. (A) RNAi of sbp-1 or a reduced function mutation of sbp-1 reduces satiety quiescence. (B) fat-6; fat-7 double mutants show reduced quiescence compared to wild type (+) after 12 hrs of fasting and 6 hrs of subsequent refeeding. (C) 6 hrs of refeeding on oleic acid (OA, 600 μM) restores normal quiescence to fat-6; fat-7 double mutants and to reduced-function mutants of sbp-1. (D) Under conditions where wild type worms are rarely quiescent, oleic acid (OA, 600 μM) induces significant quiescence (see Materials and Methods). For satiety quiescence test, 10 mutants and 10 con-current wild-type animals were tested. The experiments were independently repeated three times. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t test. (E,F) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) regulates fat storage and satiety quiescence. (E) pod-2 mutants have reduced satiety quiescence. 10 mutants and 10 con-current wild-type animals were tested. The experiments were independently repeated three times. ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t test. (F) pod-2 mutants have reduced fat storage. More than 20 mutants and 20 wild type animals were tested. The experiments were independently repeated three times. ***p < 0.001 by Student’s t test. (G) Seven transcription factors have their binding sites on the putative promoters of 19 NHRs among the 28 NHRs. The transcription factors are color-coded and the binding sites are shown for each NHR gene.