Fig. 1.
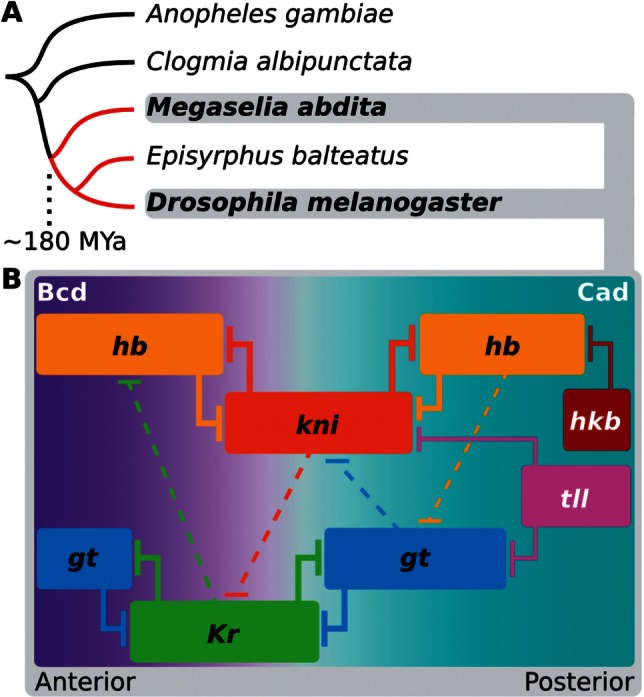
Dipteran phylogeny and structure of the gap gene network. (A) Phylogenetic position of Megaselia abdita compared with other dipteran species in which gap genes have been studied. Cyclorrhaphan lineage marked in red. (B) The gap gene networks of Drosophila melanogaster and M. abdita share the same qualitative structure. Colored boxes indicate position of gap gene expression domains along the anterior–posterior axis; only the trunk region of the embryo is shown; anterior is to the left, posterior to the right. Trunk gap genes: hb, Kr, gt, kni; terminal gap genes: tll, hkb. Background color represents main activating inputs by maternal morphogen gradients: Bcd and Cad. T-bars represent repression; dashed lines indicate net repressive interactions between overlapping domains.
