Figure 3.
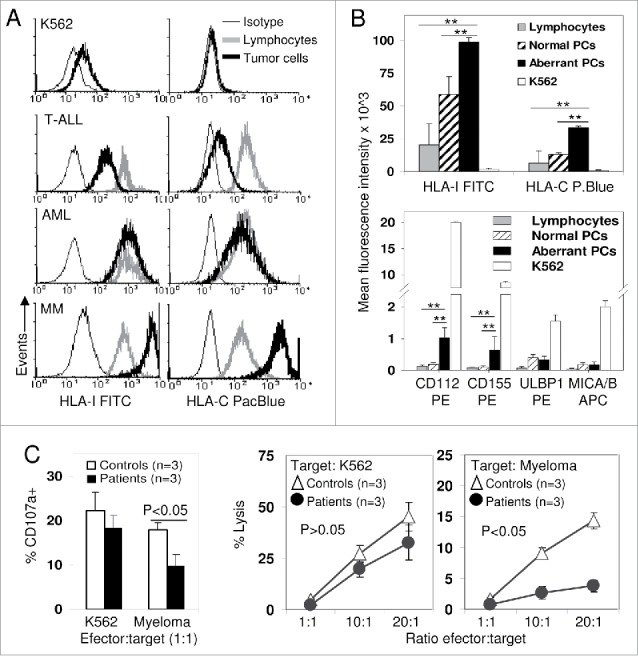
Increased expression of HLA-I (“Increasing self”) determines that myeloma plasma cells lysis mainly depends on NK cell licensing. (A) Expression of total-HLA-I (W6/32 antibody, left column) and HLA-C (DT9 antibody, right column) was evaluated in K562 cell line and in residual normal bone marrow lymphocytes (gray line) and tumor cells (bold black line) from T acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL), acute myeloblastic leukemia (AML) and MM patients. Cells were also stained with isotype control (thin line). K562 and T-ALL blasts completely or partially lost expression of total-HLA-I and HLA-C; AML blasts conserved normal expression of both molecules, but myeloma PCs showed an increased expression of both total-HLA-I and HLA-C compared to normal lymphocytes. (B) Plasma cells from myeloma patients (black bars, n = 15) showed higher expression (Mean fluorescence intensity) of total-HLA-I and HLA-C as well as ligands for activating receptors CD112 and CD155 than PCs from normal donors (striped bars, n = 10) and normal residual lymphocytes (gray bars, n = 15). K562 (white bars) showed much lower expression of HLA-I and HLA-C, and much higher expression of activating ligands than myeloma PCs. **, indicates p < 0.01 in the DMS post-hoc analysis from the ANOVA comparing both normal PCs and residual lymphocytes with myeloma PCs. (C) Ex vivo, un-stimulated purified NK cells from three individuals with variable number of iKIR2D/HLA-C licensing interactions (Controls, white bars and symbols) and three patients with no conventional iKIR2D/HLA-C licensing interactions (KIR2DL1−L2+L3−/C2C2, black bars and symbols) showed similar degranulation and cytotoxic capacity against K562 cell line. However, patients with no conventional iKIR2D/HLA-C licensing interactions showed lower degranulation (p < 0.05) and cytotoxicity (p < 0.05) activity against myeloma PCs (n = 3), cryopreserved from two C2C2 and one C1C1 MM patients. Data represent mean ± SEM of three independent experiments performed for every patient or control against every myeloma PC target. NK cells from controls showed at least one iKIR2DL licensing interaction either for C1C1 or C2C2 myeloma targets.
