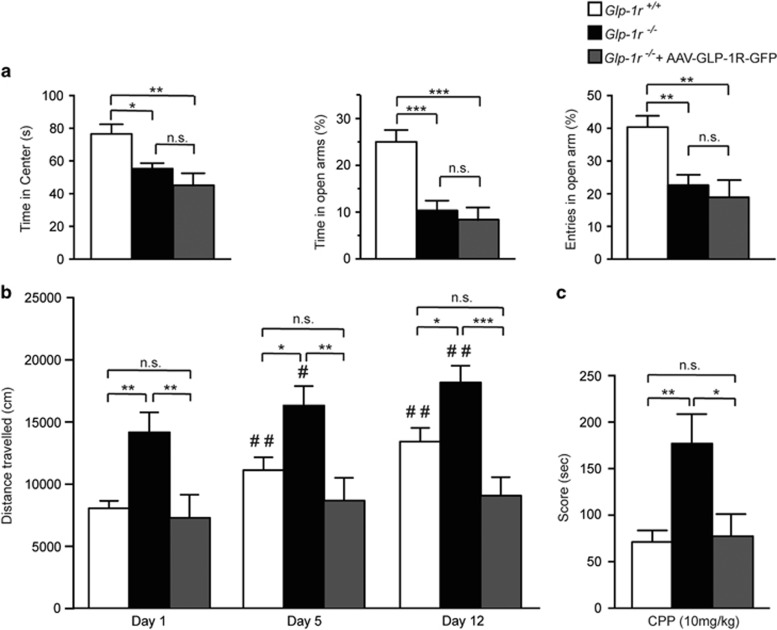
Figure 4.
Genetic complementation of GLP-1R expression in the dLS rescues cocaine-induced, but not anxiety-related, behaviors in Glp-1r-deficient mice. (a) Glp-1r−/− mice and Glp-1r−/− mice injected with AAV-GLP-1R-GFP spent less time in the center of the EPM (left panel, one-way ANOVA F=8.049; P=0.0012); Glp-1r+/+ controls (n=17) compared with Glp-1r−/− mice (n=15; P<0.05), or Glp-1r+/+ controls compared with Glp-1r−/−+AAV-GLP-1R-GFP (n=9; P<0.01). Middle panel: Glp-1r−/− mice and Glp-1r−/− mice injected with AAV-GLP-1R-GFP spent less time in the open arms (one-way ANOVA F=14.34; P<0.0001) compared with Glp-1r+/+ controls (P<0.0001) and entered the open arms less frequently (right panel; one-way ANOVA F=9.65; P<0.001; post hoc test P<0.01). (b) Altered locomotor response to cocaine for all groups over the course of the paradigm (two-way repeated measures ANOVA genotype effect F(2, 41)=9.771, P=0.0003). There was no difference between genetically complemented Glp-1r−/− mice (n=9) and Glp-1r+/+ controls (n=17) following acute cocaine exposure (day 1; P>0.9999). Intact development and expression of cocaine sensitization (two-way repeated measures ANOVA cocaine effect F(2, 82)=21.00, P<0.0001) was present in Glp-1r+/+ and Glp-1r−/− mice (n=15) but absent in Glp-1r−/−+AAV-GLP-1R-GFP mice (day 1–day 5, P=0.5141 and day 1–day 12, P=0.2919). Note that there was no difference between Glp-1r+/+ controls and Glp-1r−/−+AAV-GLP-1R-GFP on any given day. #P compared with day 1; *P compared with all groups on a given day. (c) Genetically complemented Glp-1r−/− mice displayed a normal CPP phenotype (one-way ANOVA F=7.037, P=0.0023. The CPP score represents the difference between the time spent in the cocaine compartment before and following conditioning. * or #P<0.05, ** or ##P<0.01, ***P<0.001.